These days, we hear a lot about cyber problems like hacking and fake emails. Because more things are connected to the internet, like phones and remote work setups, companies need to make sure their security plans match their business goals.
According to Gartner’s projection, around 60% of organizations will adopt a zero-trust security strategy by 2025. In career prospects, upskilling your knowledge in zero trust can be beneficial in clearing up the AZ-900: Microsoft Fundamentals exam.
This zero-trust architecture article delves deep into the origins of the zero-trust concept, its core principles, how it works, and use cases of the zero-trust model.
Let’s dig in!
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero trust refers to the strategic approach employed in cybersecurity to offer security to an organization by eradicating implicit trust and validation of digital interaction occurs at every stage.
Choosing Zero Trust means using smart tools and rules that make things both safe and flexible for the company.
The concept of the zero-trust security model involves a cybersecurity strategy where access to an organization’s digital assets is not assumed and is instead granted selectively based on user and device authentication.
This approach ensures that authorized users and devices have specific access to the necessary applications, data, services, and systems essential for their roles.
The zero trust model follows a “never trust, always verify policy” to allow only trusted individuals to access critical data.
Zero trust architecture ensures the security of the network through the following methods:
- Robust authentication techniques
- Network segmentation
- Prevention of lateral movement
- Layer 7 Threat Prevention
- Usage of least access policies
Also Read: Overview of ARM Template: Azure Resource Manager Template
Why the Zero Trust Model?
Adopting Zero Trust Model means using technology and methods that make businesses flexible and secure. Here’s why it matters:
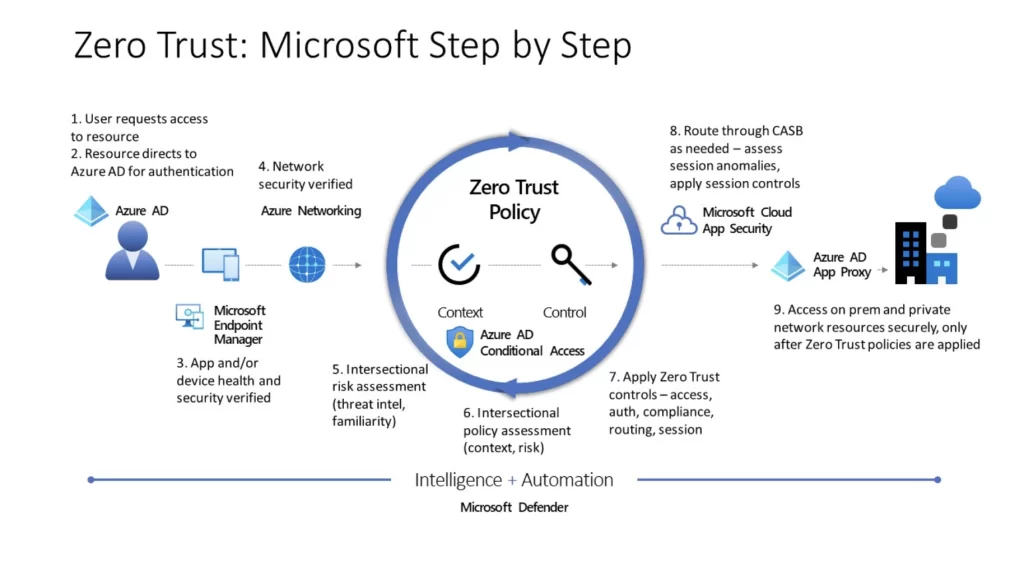
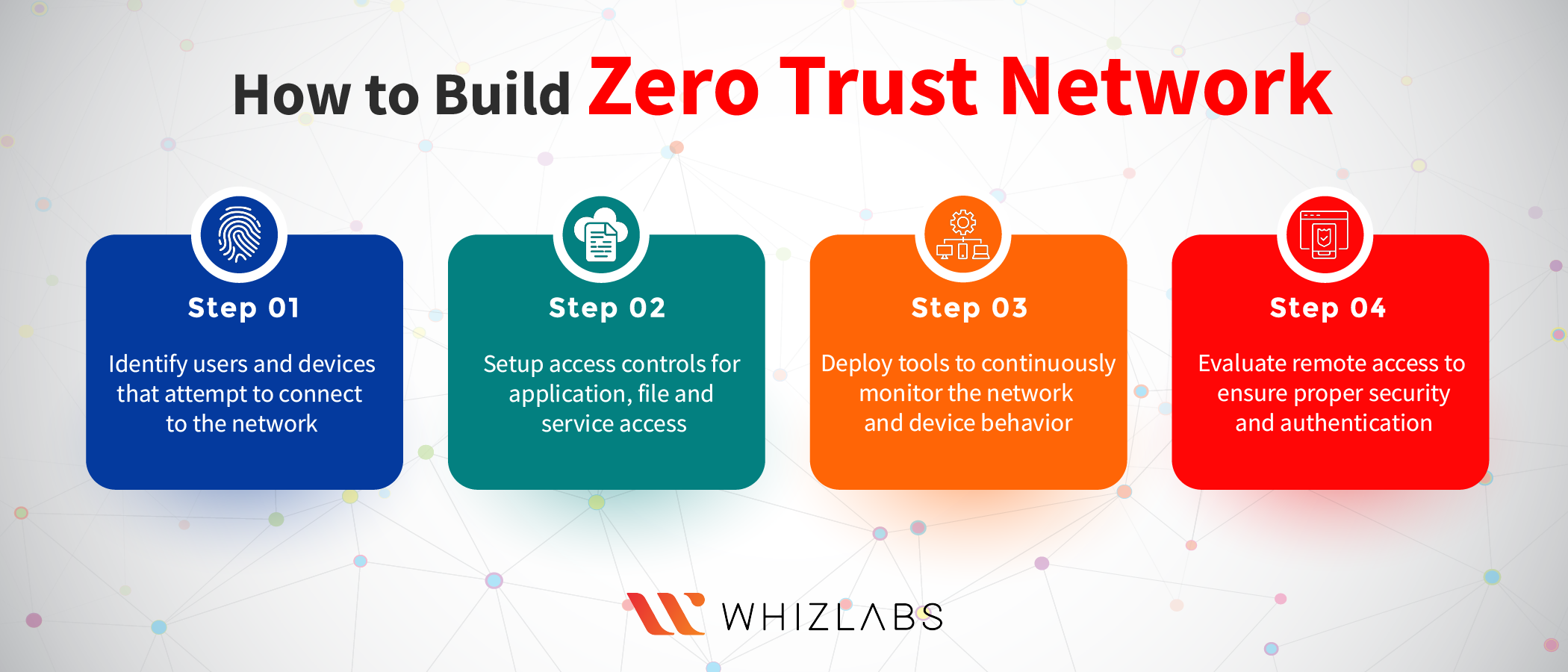
How Zero Trust Works?
The main idea of zero trust is pretty straightforward: assume that everything might be a potential threat right from the beginning. This is a big shift from the old way of securing networks, which focused on protecting a central hub and a safe boundary around it.
This older approach used things like approved codes and pathways to decide who’s allowed in, including people who connect using remote access tools.
But with zero trust, all data is moving around, even if it’s already inside the safe zone, and it is treated with caution. For instance, computer tasks are not allowed to communicate unless they prove themselves using a unique ID or user details.
This kind of security based on identity makes sure things stay safe no matter where they go—like if they’re in a cloud, a mix of systems, or even on a personal computer.
Also Read: How to Implement a Zero Trust Architecture: A step by step guide
What’s cool is that zero trust doesn’t care where things are. It keeps apps and services safe as they move between different places. Moreover, it doesn’t need to change how things are set up or follow strict rules.
Zero trust architecture makes sure that users, devices, and apps can be connected safely, no matter the network they’re in and thus achieving digital changes safer and smoother.
Core Principles of the Zero Trust Architecture: AZ-900 Certification
Zero trust architecture represents more than just user authentication, network segmentation, and secure entrance points. It’s a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that lays the foundation for an entire security ecosystem. The zero trust model revolves around three fundamental principles in AZ-900:
1. Continuous Verification: This kind of verification means forsaking trust in specific zones, credentials, or devices, hence the motto will be “Never Trust, Always Verify.” To ensure ongoing verification across an expansive array of assets, a few critical components are considered and they are:
- Risk-Based Conditional Access: This approach guarantees that workflows are only interrupted when risk levels change. This kind of approach allows for perpetual verification without compromising user experience. This means that validation is prompted only when a situation warrants it, maintaining security without causing undue disruptions.
- Swift and Scalable Dynamic Policy Deployment: With frequent migrations of workloads, data, and users, policies must not solely consider risk, but also accommodate compliance and IT requisites. While Zero Trust doesn’t exempt organizations from these obligations, its strength lies in adapting policies to the evolving landscape.
2. Limiting Radius of Breaches: In the event of a breach, securing the network becomes paramount. Zero Trust serves to restrict an attacker’s access to credentials or entry points and thus achieving affordability to systems and personnel the opportunity to respond and mitigate the assault.
- Identity-Driven Segmentation: Unlike conventional network segmentation, Zero Trust employs segmentation based on identities which can be operationally cumbersome due to frequent fluctuations in workloads, users, data, and credentials, Zero Trust employs segmentation based on identities. This provides a more agile and adaptable means of enforcing boundaries.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Whenever credentials are deployed, even for non-human entities like service accounts, it is essential to extend the permissions only to the bare minimum necessary for task execution. Overprivileged service accounts are often targeted in attacks due to under-monitoring and excessive permissions.
3. Automated Context Gathering and Response: To make sound decision-making, the availability of comprehensive data is significant, as long as it can be swiftly processed and acted upon in real time. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) offers insights on how to utilize the data from these sources:
- User Credentials: This includes both human and non-human credentials, covering service accounts, non-privileged accounts, and privileged accounts, including Single Sign-On (SSO) credentials.
- Workloads: Making use of virtual machines (VMs), containers, and hybrid deployments of workloads helps in understanding the operational environment.
- Endpoints: All devices employed for accessing data contribute to contextual insights, aiding in informed decisions.
- Network: The network landscape is a valuable source of information and it helps to know the traffic patterns and potential anomalies.
- Data: Understanding data flow and usage is necessary for comprehensive protection.
- Additional Sources via APIs: Supplemental information can be gathered from sources like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Single Sign-On (SSO) providers, and identity management systems like Active Directory (AD).
- Threat Intelligence: Relying on external threat intelligence sources further enriches the contextual understanding and enhances response capabilities.
Know More : Free AZ-900 Exam Questions on Microsoft Azure Exam AZ-900 Certification
Use cases of Zero Trust Architecture: AZ-900 Certification
Zero trust architecture, a comprehensive cybersecurity approach, offers several practical applications:
Reducing Business and Organizational Risk
Zero Trust ensures that applications and services only communicate when their identity attributes are verified when they are aligned with trust principles like authentication and authorization.
By uncovering network assets and monitoring their interactions, a zero trust approach can minimize risks. It establishes baselines and further reduces risk by eliminating unnecessary software and continuously validating the “credentials” of every communicating element.
Gaining Control in Cloud and Container Settings
When dealing with cloud environments, concerns about access management and visibility are common. Zero Trust applies security policies based on the identity of interacting workloads, closely tied to the assets themselves. This proximity to protection remains constant despite changes in the environment, ensuring security is maintained even in cloud scenarios.
Mitigating Data Breach Risks
Zero Trust follows the principle of least privilege and treats every entity as potentially hostile. Requests are carefully examined, users and devices authenticated, and permissions evaluated before granting any “trust.”
This Zero trust architecture trust is consistently reassessed as contextual factors shift, such as user location or accessed data. This stringent approach blocks attackers from accessing or stealing data and eliminates lateral movement within networks.
Assisting Compliance Efforts
Zero Trust keeps user and workload connections hidden from the internet to safeguard them from exposure or exploitation. This invisibility streamlines the demonstration of compliance with regulatory standards like PCI DSS and NIST 800-207.
The implementation of Zero Trust micro-segmentation creates boundaries around sensitive data, aiding in separating regulated and non-regulated information. This setup enhances visibility and control, resulting in fewer compliance issues during audits or data breach incidents.
Read More: Expert Tips for Acing the AZ-900 Exam
FAQs
What are the 5 pillars of the Zero Trust Model?
- Identity
- Devices
- Network
- Data and Applications
- Workloads
Can you give an example of zero trust?
Here are four cases showing how zero trust enhances security:
- Third-Party Access: Ensuring external entities meet stringent verification for resource access.
- Multi-Cloud Remote Access: Consistent access controls across various cloud platforms.
- IoT Security: Authenticated and monitored interactions for IoT devices.
- Insider Threat Prevention: Detecting unusual user and device behavior early on.
What are the components of Zero Trust architecture in AZ-900 Certification?
The core components of zero trust architecture are:
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Microsegmentation
- Trust Zones and Default Access Controls
Conclusion
Hope this zero trust architecture article covers everything about the core principles of zero-trust architecture AZ:900 and the importance of zero trust in today’s digital transformation.
And also you have gained detailed insights into the Zero trust model, zero trust principles and how the zero trust architecture works, and use cases of zero trust.
To further enrich your understanding of zero trust architecture in practice, try our Azure hands-on labs and Azure sandboxes.
If you have any doubts about this blog post, please feel free to comment to us!
- Study Guide DP-600 : Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric Certification Exam - June 14, 2024
- Top 15 Azure Data Factory Interview Questions & Answers - June 5, 2024
- Top Data Science Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - May 30, 2024
- What is a Kubernetes Cluster? - May 22, 2024
- What are the Roles and Responsibilities of an AWS Sysops Administrator? - March 28, 2024
- How to Create Azure Network Security Groups? - March 15, 2024
- What is the difference between Cloud Dataproc and Cloud Dataflow? - March 13, 2024
- What are the benefits of having an AWS SysOps Administrator certification? - March 1, 2024