Test driven development – TDD, as its name describes is based on test first approach. Tests drives the development. In a very simple language Test Driven Development is nothing but frequent or fast cycles of testing, coding and refactoring with testing before coding. The speed of these cycles is such that it’s not possible to do so in a manual way. Therefore TDD is a computer programming based methodology that consists of small rapid iterations.
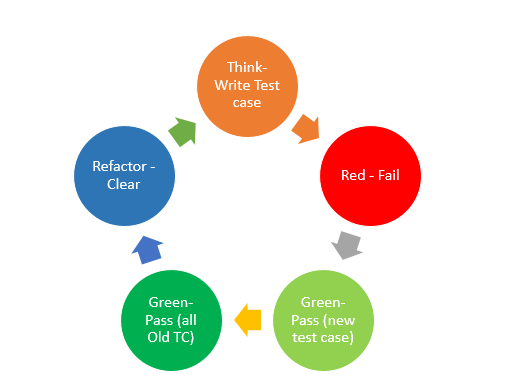
TDD has the following steps:
- Think & write test cases
- Red – Failure of test case
- Green – Code and get the new test case pass
- Green – Ensure all old test cases also pass
- Refactor the code to clean it
- Repeat this cycle
As shown in this diagram, all these steps go in rounds. This method starts with writing the test cases for the newly identified functionality, after that production code necessary to make the test pass is written and after that code is refined by doing refactoring so that code is more maintainable. As we have written the tests before writing the code, it ensures we get immediate feedback after changes are made. TDD (test-driven development) is a technique for designing the software as well as testing it.
- Think & write test case: In this step developer writes the test case without any code in front him. This is tricky, but ensures that the developer understands the functionality required and accordingly write the test case. The test case is not biased to show code works rather test cases are to test the expected feature
- Red – Failure of test case: In this step, you try to run the test case. As there is no code, you will get compile error itself. This is referred as Red stage indicating failure of test case
- Green – Code and get the new test case pass: In this step, the developer writes only the minimum required code to pass the test case just got failed. This becomes a challenging activity for developer who are used of writing code for the full module in one go. “Just enough” code concept helps in ensuring that no extra bit of code is going in. Developer again run the test case and make sure it passes
- Green – Ensure all old test cases also pass: Step 3 & 4 generally happens in one go. To make the understanding clear its bifurcated hire developer while testing the newly written code has to ensure that no old test case fails. This is nothing but continuous regression.
- Refactor the code to clean it: In this step developer refactor the code to ensure the functionality is intact and code is refined. In step 3 & 4 the focus is to write code only, whereas other important points for efficient design, maintainable code etc. are not considered. Refactor ensures it.
- Repeat this cycle: Step 1 to 5 are repeated multiple times in an automated manner so that all the features are covered in TDD cycles.
- What are Scrum roles and why it’s needed? - August 12, 2017
- Stakeholder Analysis – Is it required? - July 28, 2017
- Project Manager – An integrator, how? - July 28, 2017
- Different PMI Certifications – Which one to choose? - July 28, 2017
- What is the importance of Change Management in Project Management? - June 23, 2017
- What’s important to know to build a career in Agile? - June 23, 2017
- Agile Basics, Manifesto & Principles - June 23, 2017
- Scrum – Is it mandatory to learn in today’s IT market? - June 2, 2017
good