The Google Cloud Console serves as the central hub for managing and administering the GCP resources. From computing and storage to databases, machine learning, and beyond, the console offers a unified as well as intuitive interface for administering the cloud infrastructure.
Google Cloud console is mainly used to perform simple storage management tasks for the Cloud Storage and thus transition to this console can lead to effective data storage.
In this article, we will delve into the Google Cloud console, features of Google Cloud Console, tasks carried out in Google Cloud Console, and supporting platforms of GCP.
Let’s dive in!
What is the Google Cloud console?
In general, the Google Cloud console is a web-based GUI used to manage Google Cloud-based projects and resources. When you use the Google Cloud console, you either create a new project or choose an existing project, and then utilize the resources that are required to create in the context of that project.
Also Read: Top 10 Highest Paying Cloud Certifications in 2023
You can use a web browser to manage the files and execute simple storage operations using the Google Cloud dashboard. You must be authenticated with Google and have the necessary permissions to carry out a specified task in order to access the Google Cloud console.
It’s likely that you possess all the necessary permissions to accomplish the tasks listed below if you’re the account owner who initiated the project. Alternatively, you can be allowed authorization to work on a bucket or access to a project.
The Google Cloud Platform has very advanced data privacy and security capabilities. When GCP support agents or system engineers communicate with the information you provide and Access Transparency keeps logs of those interactions in almost real-time. In the same way, Access Approval, which is currently in testing, enables customers to actively authorise or deny Google administrators access to stored data or configurations.
Google now provides managed versions of open-source software from partners like MongoDB, Confluent, Elastic, InfluxData, and Redis Labs in response to demand.
An earlier gap between Google and Amazon’s AWS Lambda has been closed by Google’s developed serverless computing technology. Serverless solutions from Google Cloud Platform are available for a range of tasks, including app development, analytics, workflow design, and more. Elastic Cloud is also integrated into it to allow open source search and analytics.
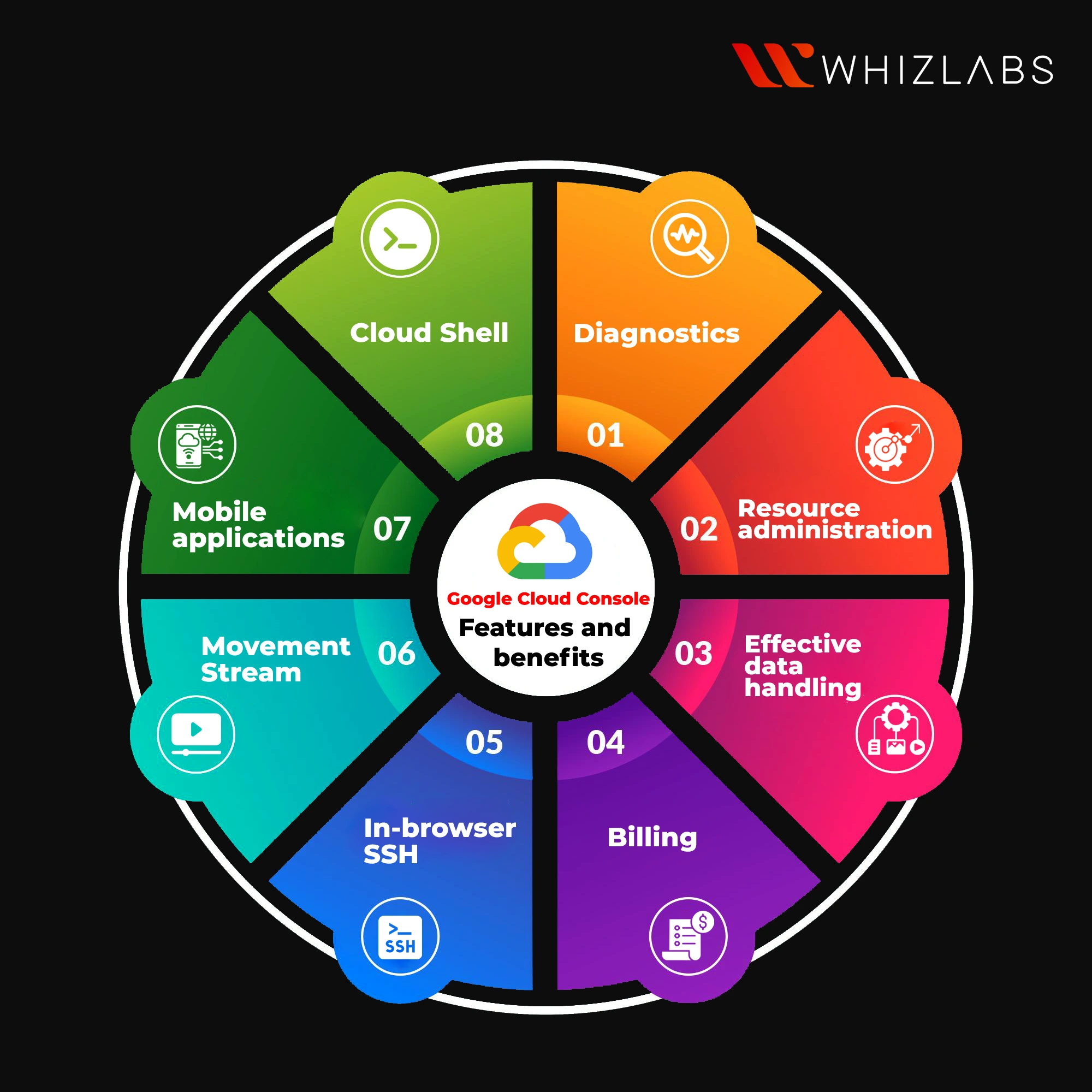
Google Cloud Console : Features and benefits
Here are some unique features of Google Cloud Console:
Resource administration: Find and quickly assess the condition of all the cloud resources, such as virtual machines, network configurations, and data storage, in one location.
Effective data handling : Big and little data processing, storing, and querying can be done easier on this platform.
Billing : You can be able to view a thorough analysis regarding your latest bill. Set budgets for expenses to prevent surprises.
In-browser SSH: Direct SSH connections from the browser to the virtual machine instances can be made in a quicker and secured way.
Movement stream: In one location, you can see every activity taken on in the cloud’s applications. View the project updates made by your colleagues to find problems and audit access.
Mobile applications: Mobile console native applications for iOS and Android allow you to perform DevOps chores while on the go.
Cloud Shell: The cloud-based admin machine is called Cloud Shell. Use this instant-on Linux box to perform power jobs with ease. It comes pre-configured, authorized, and with all of your favorite tools, including the cloud SDK.
By eliminating the need for setting up the Google Cloud SDK and other tools on your machine, it makes it simple for you to manage your initiatives and resources. The Cloud SDK command-line tool and other tools are accessible with Cloud Shell when you require them.
Diagnostics: You can find production problems as soon as possible. The logs viewer makes it simple to quickly browse and filter through all of your instances’ real-time logs. You can speed up the application and utilize fewer resources by using Cloud Trace, which provides thorough latency information. You can access local variables and a complete stack trace at any point and line number using Cloud Debugger.
Administration: Admin Control and monitor staff members’ utilization of project resources.
Tasks carried out in Google Cloud Console
Some of the tasks that are carried out in Google Cloud Console have been explored below:
- Examine the condition of the resources you have on Google App Engine, Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, and Cloud SQL.
- Verify billing information and cost projections
- To get a quick overview of your solution, design your own unique dashboard
- Use your device to do simple operations like rebooting a virtual machine
- Keep an eye out for application issues.
- View and control incidents that Google Cloud Monitoring has tracked
- Observe the latency trace data
Bucket creation
Although Google Cloud Console allows you to create folders and simulate a folder structure, Cloud Storage employs a flat namespace to store information. Although your data doesn’t seem actually kept in a hierarchical format, the Google Cloud dashboard presents it that way.
The folder suffix and product name boundaries are apparent when you examine the folders you have created using the gcloud CLI or any of the other command-line tools that might be compatible with Cloud Storage since Cloud Storage has no concept of folders.
Data uploading into bucket
The user can upload one or more files, or a location containing files, to the bucket in order to add data. The Google Cloud dashboard preserves the folder’s organisation when you upload it, containing all of the documents and folders it holds. The upload progress window allows you to monitor the status of downloads to the Google Cloud interface. You can close your progress window and carry on using your bucket while doing so.
By simply dropping and dragging folders and files from the desktop or file manager application to a bucket or subfolder, you can also download things to the Google Cloud dashboard.
Using and creating folders
Folders defined in the Google Cloud dashboard are an utility to help you organize objects in a bucket since the Cloud Storage system does not include the concept of folders. The Google Cloud console displays folders using a folder icon image as a visual aid to assist you in differentiating folders from objects.
In the Google Cloud console, items uploaded to a folder appear to be stored there. All items actually reside at the bucket level and just have names that reflect the directory structure. The Google Cloud dashboard will make the file appear to be present in the folder, for instance, if you establish a folder called pets and add the file cat.jpeg to it.
Folders are not required to be globally unique as buckets do. To put it another way, folder names may be used again as long as they don’t belong in the same bucket or sub-folder, unlike bucket names, which are limited to usage if there are no buckets with the same name already in use.
When exploring directories in the Google Cloud dashboard, choosing the appropriate folder or bucket title in the breadcrumb navigation trail over the file listings will take you to a higher level of the directory.
The way folders are displayed while working with the buckets and data using other tools could differ from how they are displayed in the Google Cloud dashboard. To learn more about how various tools, including the gcloud CLI, imitate folders in Cloud Storage.
Viewing buckets or items through filtering
You may utilise the Filter buckets text box to limit the buckets you see in the list of bucket for a particular project in the Google Cloud dashboard. You may always use the bucket name prefix as a filter.
You are able to filter by additional parameters, such as the address of buckets, for projects with fewer than 1000 buckets.
Use the choice that displays next to the filtering text box to enable extra criteria filtering for tasks with more than 1000 buckets. However, keep in mind that when additional criterion filtering is set, projects with thousands of buckets experience decreased filtering speed.
Setting object metadata
The metadata for an object can be set up in the Google Cloud console. Elements of how requests are processed are controlled by object metadata, including the kind of content represents and how it is encoded. Setting the information for one object at a time using the Google Cloud console. To set metadata on numerous items at once, you can use gcloud storage objects.
Deleting files, buckets, and directories
By clicking the box next to any bucket, folder, or item in the Google Cloud console, clicking the Delete button, and then confirming your decision to move forward, you can delete it. All items contained in a folder or bucket, even those marked as public, are also deleted when the folder or bucket is deleted.
Data sharing
A link icon displays in the object’s public access section when you share it publicly. The link provided provides a public URL to access the object when clicked.
The link that appears when you right-click an object directly differs from the public URL. Both links go to the same object, but only the public URL may be used without logging into a Google account.
Setting bucket permissions
IAM permissions can be used to restrict access to a Cloud Storage bucket. For instance, you can configure a bucket’s permissions to permit a user or group to see or add objects to the bucket. When adding a user at the project’s level is not appropriate, you might use this method. When attempting to access the bucket, the entity defined in the IAM authorization must first authenticate by logging into Google.
Working with Object Versioning
Enabling item Versioning raises storage costs, but it allows you to keep older versions of an item in case it gets accidentally deleted or replaced. When you enable Object Versioning, you can reduce expenses by incorporating Object Lifecycle Management criteria. Based on the settings you choose, these conditions automatically remove or declassify previous object versions.
Using Cloud Data Loss Prevention to scan buckets
A service called Cloud Data Loss Prevention (Cloud DLP) enables you to locate and safeguard sensitive data in your buckets. Cloud DLP can assist you in complying with regulations by locating and removing data like: credit card numbers, an IP address and additional types of personally identifiable data.
Google cloud Supported browsers
The Google Cloud console can be used in the following browsers:
- Chrome
- Safari
- Firefox
- Edge
FAQs
What is Google Console Cloud?
The user can be able to deploy, scale, and troubleshoot production issues using the Google Cloud console’s user-friendly web interface.
Is Google Cloud API free?
The Google Search Console API is free of charge. But it may be subject to some usage limits.
What is the Google API’s limit?
It can be changed up to a maximum value of 1,000 requests per user every 100 seconds, which is the default setting. However, each user is only permitted to make a maximum of 10 queries per second to the API.
What is the difference between the Google Cloud console and cloud?
Well, Cloud Shell and GCP Console differ in terms of their installation and interface. Cloud Shell is a locally installed tool, while GCP Console operates as a temporary virtual machine. It is worth noting that although these tools serve similar purposes, they have distinct characteristics. GCP Console offers a graphical user interface, while Cloud Shell is a command-line tool.
Is Google Cloud same as Azure?
Comparison: Azure vs Google Cloud Storage Services In terms of storage services, Azure and Google Cloud have distinct strengths. Azure offers a comprehensive range of storage services and features, although it may have a steeper learning curve, particularly for users unfamiliar with Microsoft technology. On the other hand, Google Cloud offers a more streamlined set of features but stands out in terms of storage pricing and user-friendliness.
What is the use of Google Cloud console?
With the Google Cloud console, you can effortlessly deploy, scale, and troubleshoot production issues using a user-friendly web-based interface. Its search functionality enables swift resource discovery, and you can conveniently connect to instances directly through the browser using SSH.
What is GCP for beginners?
Google Cloud Platform is a collection of Google cloud computing services that allows you to store, manage, and analyze data. It is also used to develop, launch, and scale applications on Google’s platform.
Is GCP exam tough?
The GCP Associate Cloud Engineer exam is considered to be of moderate difficulty.
Is GCP harder than AWS?
In general, GCP exams are easier than AWS and Azure, and if you’re certified for AWS and Azure, you should have no trouble passing the same GCP exams if you put in the same amount of study time.
Conclusion
Hope this google cloud console article has helped to gain a deep understanding of the features and capabilities offered by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). And also we explored the various components of the Google Cloud Console, enabling you to navigate the platform with higher levels of confidence and unlock its full potential.
As you continue your journey with Google Cloud, remember that Google cloud platform is continually evolving, with innovative services and features being introduced regularly.
Stay updated with the latest developments, explore google cloud console documentation,hands-on labs, sandboxes and engage with the vibrant community to expand your knowledge and make the most of GCP.
- Top 25 AWS Data Engineer Interview Questions and Answers - May 11, 2024
- What is Azure Synapse Analytics? - April 26, 2024
- AZ-900: Azure Fundamentals Certification Exam Updates - April 26, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Data Engineer Associate Certification - April 19, 2024
- Maximizing Cloud Security with AWS Identity and Access Management - April 18, 2024
- A Deep Dive into Google Cloud Database Options - April 16, 2024
- GCP Cloud Engineer vs GCP Cloud Architect: What’s the Difference? - March 22, 2024
- 7 Ways to Double Your Cloud Solutions Architect Role Salary in 12 Months - March 7, 2024