One of the foremost players in the cloud service vendor market is Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The expertise of Google in running data centers is an undeniable fact, isn’t it? After all, it runs the world’s top search engine! After the launch of AWS in 2006, Google implemented its data center expertise for launching its own cloud service.
And today, it is one of the three prominent players among public cloud vendors alongside AWS and Microsoft Azure. The following discussion provides a Google Cloud cheat sheet for obtaining a basic understanding of Google Cloud Platform. The important elements in the discussion include an introduction of GCP along with its history and architecture.
Preparing to become a certified Google Cloud professional? Check our Google Cloud Certifications Training Courses now!
The discussion would also highlight the advantages of GCP and different approaches for working on Google Cloud Platform. Furthermore, the Google Cloud platform cheat sheet would provide brief outlines of important terms, services, products, and commands. In addition, the discussion would also illustrate the list of important certifications by Google Cloud Platform.
Google Cloud Cheat Sheet: Terms, Definition, and Glossary
As we start the Google Cloud Cheat Sheet, it is important to understand terms and definitions related to the Google Cloud Platform and cloud computing. Let’s understand some common terms, definition, and glossary.
Cloud Computing: The delivery of IT resources and services through a network rather than from on-premise resources.
Cloud Migration: The process of transferring applications, data, and services from on-premise systems to the cloud.
Cloud Service Provider (CSP): Any company which sells cloud computing services, either PaaS, IaaS or SaaS.
Container: A virtual instance with the facility of multiple isolated user-space instances allowed by the kernel of an operating system.
DevOps: A methodology derived from the combination of development and operations teams that promotes communication, collaboration and integration among them.
Google Cloud Platform: GCP is the cloud service offering of Google that provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) products.
Host Machine: The server or physical machine which stores containers or virtual machines.
Hybrid Cloud: Cloud computing environment developed with a combination of public and private clouds alongside on-premises solutions.
Instance: A single virtual machine or server supporting a particular workload.
Multi-tenancy: Model of software operation that facilitates running of multiple instances of one or more applications in a shared environment.
Google Cloud Platform
Presently, every other Google cloud cheat sheet you search will show Google on the third or fourth rank among public cloud vendors. It is one of the tough competitors to Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM. The definition of Google Cloud Platform varies from one source to another. However, the most general notion about GCP is that it is the collection of cloud computing services provided by Google.
The architecture of GCP is based on the infrastructure used by Google internally for end-user products such as YouTube and Google Search. A brief reflection on the history of GCP could establish the foundation for proceeding towards a discussion on GCP’s architecture.
Know More about GCP: https://www.whizlabs.com/blog/google-cloud-platform/
History of Google Cloud Platform
The origins of GCP serve as one of the crucial elements in every Google cloud cheat sheet. However, mere information about the launch date of GCP is not enough! It is important to note that Amazon and Microsoft ventured into the cloud with IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) offerings. On the other hand, Google started off with a PaaS (Platform as a Service) offering known as the App Engine.
In April 2008, the first preview of the App Engine was available for developers. In the initial stage, only 10,000 users had the preview of the App Engine. As of May 2008, the number of users reached 75,000, and over 80,000 were on the waiting list. At that point in time, Google let the service open for everyone, and resources were free, albeit limited.
In 2009, Google introduced the option for purchasing resources other than the ones in the free tier. Subsequently, the preview label on App Engine was no more in November 2011. The first bit of criticism came for Google due to the lack of support for popular programming languages such as Java. Google worked on the issue in April 2009 after the initial reviews.
The next important aspect of the history of GCP in this Google Cloud Platform cheat sheet is the second phase. Google came up with the second most popular cloud service known as Cloud Storage in May 2010. This was the first venture of Google into the IaaS market. At that point in time, Google also brought in support for enterprise users with the launch of Google App Engine for Business.
Subsequently, Google introduced Compute Cloud live as a preview in June 2012 as a competitor for Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines and AWS Elastic Compute Cloud. The development of GCP since then has been possible through the introduction of new services. However, it also continues to be a public cloud provider with the least prices alongside additional advantages of big data, container management, and machine learning tools.
The Architecture of the Google Cloud Platform
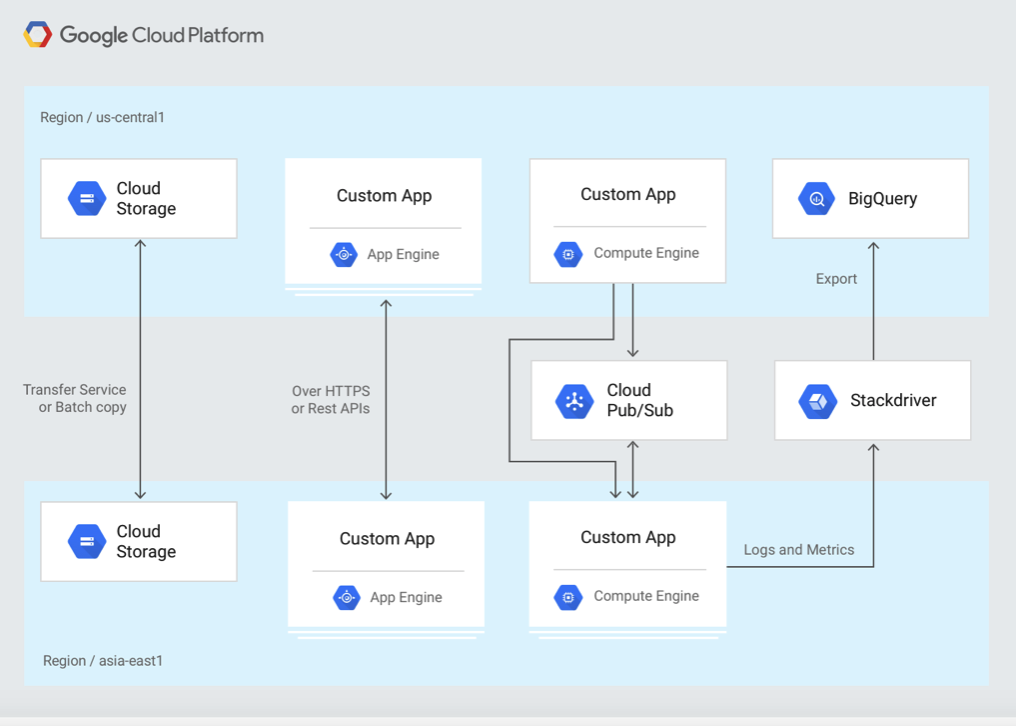
The next important element in this Google Cloud cheat sheet is a brief outline regarding the architecture of the Google Cloud Platform. Basically, the Google Cloud Architecture follows multitenancy. It is a variant of computing architecture that involves the creation of one or more logical software instances alongside executing them on top of primary software. The multitenant architecture enables multiple users to work in a software environment concurrently with separate user interfaces, services, and resources. So, how does the architecture of GCP help users?
Benefits of Google Cloud Platform
The benefits of GCP are also a staple inclusion for every Google cloud developer cheat sheet. This list of Google Cloud Platform benefits form the basis of reasons to adopt Google Cloud Platform.
-
Security
Continuing from the above-stated, the multitenant infrastructure of GCP provides exceptional security during service deployment. Security is the prominent concern for the deployment of applications on GCP’s infrastructure. There is no assumption of trust between services, and multiple mechanisms help in establishing and maintaining trust. Other crucial advantages in terms of security are evident in operational and device security, encryption of internet communication, identity and access management, and encryption of stored data.
-
Better Pricing
The next important advantage of Google Cloud Platform is the facility of better pricing in comparison to the competitors. The facility of billing in minute-level increments alongside discounts for long-running workloads without any up-front commitment.
-
Faster and Extended Network
The large network of Google is one of the foremost benefits. The investment of Google in the FASTER Cable System in 2016 and in the first private trans-Atlantic subsea cable in 2018 show the extensive plans of Google for expanding and strengthening its network. Furthermore, GCP introduced premium tier and standard tier networks that is the first major public cloud with a tiered cloud network.
-
Live Migration
The facility of live migration of virtual machines is also one of the common mentions in every Google cloud cheat sheet. Live migration helps in addressing issues such as patches, repairs, software, and hardware updates effectively.
-
Redundant Data Storage
The plans of Google Cloud Platform for rapid expansion, as well as the facility of redundant backups, are commendable advantages. Google Cloud Storage provides the assurance of 99.99999% durability. Google cloud developer cheat sheet contains information about different types of storage models.
The four types of storage are cold line storage, regional storage, multi-regional storage, and nearline storage. Redundant data storage with automatic checksums helps in ensuring data integrity. In addition, multi-regional storage provides the benefit of geo-redundancy. Therefore, cloud storage stores data in at least two regions so that your data is safe, even in the case of a calamity.
Preparing for Google Cloud interview? Check out these Google Cloud interview questions and get ready to ace the interview.
How to Work on the Google Cloud Platform?
Another crucial addition to every Google cloud cheat sheet is the illustration of basic steps for working on GCP. The best way to learn your baby steps on Google Cloud Platform is through some quick-start guides. The guides are actually activities that involve basic tasks.
- First of all, you can learn about the creation of a Linux VM, connect with it and then delete it. This simple task can help in learning about the Google Compute Engine.
- The next activity to learn about working on GCP in a Google Cloud developer cheat sheet is storing a file and sharing it. This activity involves the creation of a bucket, uploading a file, sharing the file, and then organizing it into a folder. You can learn about Google Cloud Storage with this activity.
- You can gain a basic impression of Kubernetes Engine and Cloud SDK with a simple task of deploying a Docker Container Image. The activity involves using Cloud Shell for configuration of gcloud and running a container image.
Other basic activities that can be important additions to every Google cloud architect cheat sheet are as follows:
- Training a TensorFlow model locally in the Cloud with a single worker and in a distributed environment for understanding Machine Learning API.
- Running label detection on an image by using the Cloud Vision API service.
- Deploying a small App Engine application by creating a Python application for a basic understanding of Google App Engine.
Products and Services on Google Cloud Platform
The most important content of every Google Cloud architect cheat sheet is the illustration of the products and services. The ever-expanding portfolio of offerings by GCP is also one of its most prominent highlights. The broader classification of Google Cloud Platform’s products and services is evident in the following categories.
- Computing and hosting
- Machine learning
- Storage
- Big data
- Networking
- Databases
-
Computing and Hosting Services
Computing and hosting services by GCP offer different options and find mention in every Google cloud cheat sheet. The options include working in a serverless environment or using a managed application platform. Users could also make the most of container technologies for additional flexibility. In addition, users also have the option of creating their own cloud-based infrastructure for ensuring maximum control. GCP’s Compute Engine is the IaaS offering that gives you a sturdy computing infrastructure. Users could choose the components they want to include.
-
Machine Learning Services
Machine learning services are also another important entry in a GCP Cheat Sheet 2020. The AI Platform of Google provides different machine learning services; Users can select APIs with pre-trained models having optimization for particular applications. On the other hand, users could also build and train their personal large-scale, comprehensive models by leveraging a managed TensorFlow framework.
Must Read: Introduction to Machine Learning on Google Cloud Platform
-
Storage Services
Google Cloud’s storage services are also a mandatory element in every Google Cloud cheat sheet. The foremost name that comes to mind with GCP storage services is Google Cloud Storage. It provides consistency, scalability alongside the large capacity for storing data. Persistent disks on Compute Engine could also be primary storage alternatives for instances. Another notable storage service that you can find in almost every Google commands cheat sheet is the Filestore. Filestore provides fully managed NFS file servers.
-
Big Data Services
Big data services of GCP are also one of the prominent elements in the Google cloud cheat sheet. Big data services include BigQuery for data analysis services, Dataflow for batch and streaming data processing, and Pub/Sub for asynchronous messaging.
-
Networking Services
Networking services are prominent entries in every Google commands cheat sheet along with other important services. It is one of the commonly used services with App Engine handling networking. The GKE implements Kubernetes Model with networking resources by Compute Engine. The networking services can help in the creation of DNS records, the connection of the existing network to Google’s network, and load-balancing traffic across resources.
-
Database Services
The final mention among the Google Cloud Platform services in a Google Cloud cheat sheet is database services. The assortment of SQL and NoSQL database services in this category of GCP offerings serves as the backbone of GCP’s popularity. Cloud SQL on GCP provides SQL database with the option of MySQL or PostgreSQL databases.
The Cloud Firestore and Cloud Bigtable are two distinct alternatives to NoSQL data storage. Users could also opt for Cloud Spanner that offers a fully managed, relational database service with transactional consistency. Other crucial features of Cloud Spanner include schemas, SQL querying, and automatic, synchronous replication to ensure high availability.
Confused while choosing a cloud hosting for your business? Here are the top advantages of Google Cloud Hosting that will benefit your business.
Products and Services on Google Cloud Platform
The following table outlines a list of the different products and services on Google Cloud Platform in different categories. The table also includes brief definitions of each product and service.
Category |
GCP product or service offering |
Definition (Functionality) |
|
Compute |
App Engine |
The managed app platform for GCP |
|
Cloud Functions |
Serverless functions according to specific events |
|
|
Cloud Run |
Serverless computing for containerized applications |
|
|
Compute Engine |
Virtual machines, disks, GPUs and TPUs |
|
|
Kubernetes Engine (GKE) |
Managed services for Kubernetes or containers |
|
|
Anthos |
Enterprise-grade multi-cloud or hybrid platform |
|
|
Storage |
Cloud Storage |
Storage and serving of objects |
|
Nearline |
Archival storage with occasional access |
|
|
Coldline |
Archival storage with rare access |
|
|
Persistent Disk |
VM-attached disks |
|
|
Cloud Filestore |
Managed service for NFS server |
|
|
Database |
Cloud Bigtable |
Low-latency, non-relational, petabyte-capacity database |
|
Cloud Datastore |
Document database with horizontal scalability |
|
|
Cloud Firestore |
Highly consistent serverless document database |
|
|
Cloud Memorystore |
Managed Redis |
|
|
Cloud Spanner |
Relational database with horizontal scalability |
|
|
Cloud SQL |
PostgreSQL and Managed MySQL |
|
|
Data and Analytics |
BigQuery |
Data analytics or warehouse service |
|
BigQuery BI Engine |
In-memory analytics engine |
|
|
BigQuery ML |
Training or serving of BigQuery model |
|
|
Cloud Composer |
Managed service for workflow orchestration |
|
|
Cloud Data Fusion |
Graphical management for data pipelines |
|
|
Cloud Dataflow |
Stream or batch data processing |
|
|
Cloud Datalab |
Managed Jupyter notebook |
|
|
Cloud Dataprep |
Visual data wrangling |
|
|
Cloud Dataproc |
Managed services of Spark and Hadoop |
|
|
Cloud Pub/Sub |
Global real-time messaging |
|
|
Data Catalog |
Management service for Metadata |
|
|
Data Studio |
Collaborative dashboarding and data exploration |
|
|
Genomics |
Managed platform for genomics |
|
|
Artificial Intelligence/ Machine Learning |
AI Hub |
Hosted services for AI component sharing |
|
AI Platform |
Managed machine-learning platform |
|
|
AI Platform Data Labeling |
Human data labelling |
|
|
AI Platform Deep Learning VMs |
Pre-configured VMs to support deep learning |
|
|
AI Platform Notebooks |
Managed instances of JupyterLab notebook |
|
|
AI Platform Predictions |
Autoscaled model service |
|
|
AutoML Natural Language |
Custom text models |
|
|
AutoML Tables |
Custom structured data models |
|
|
AutoML Translation |
Custom translation service according to domain |
|
|
AutoML Video Intelligence |
Custom video annotation models |
|
|
AutoML Vision |
Custom image models |
|
|
Cloud AI Building Blocks |
Hosted repository service for AI component |
|
|
Cloud Natural Language API |
Text parsing and analysis |
|
|
Cloud Speech-to-Text API |
Conversion of audio to text |
|
|
Cloud Talent Solutions API |
Job searching with ML |
|
|
Cloud Text-to-Speech API |
Conversion of text to audio |
|
|
Cloud Translation API |
Detecting and translating language |
|
|
Cloud Video Intelligence API |
Video annotation with respect to scene |
|
|
Cloud Vision API |
Recognition and classification of images |
|
|
Cloud TPU |
Hardware acceleration for ML |
|
|
Diagflow Enterprise Edition |
Creation of conversional interfaces |
|
|
Document Understanding AI |
Analysis, classification and search of documents |
|
|
Recommendations AI |
Creation of custom recommendations |
|
|
Vision Product Search |
Visual search for products |
|
|
Networking |
Carrier Peering |
Peering through a carrier |
|
Direct Peering |
Peering with GCP |
|
|
Dedicated Interconnect |
Dedicated private network connection |
|
|
Partner Interconnect |
Connecting on-premise network to VPC |
|
|
Cloud Armor |
WAF and DDoS protection |
|
|
Cloud CDN |
Content delivery network |
|
|
Cloud DNS |
Programmable DNS serving |
|
|
Cloud Load Balancing |
Distribution of loan in multiple regions |
|
|
Cloud NAT |
Translation service for network address |
|
|
Cloud Router |
VPC or on-premises network route exchange |
|
|
IPsec VPN |
Virtual private network connection |
|
|
Network Service Tiers |
Tiering according to price and performance |
|
|
Network Telemetry |
Network telemetry service |
|
|
Traffic Director |
Management of service mesh traffic |
|
|
Google Cloud Service Mesh |
Network management with focus on service |
|
|
Virtual Private Cloud |
Networking defined by software |
|
|
Internet of Things (IoT) |
Cloud IoT Core |
Management of devices and data ingestion |
|
Identity and Security |
Access Transparency |
Auditing access of cloud provider |
|
Binary Authorization |
Security for Kubernetes deploy-time |
|
|
Cloud Audit Logs |
GCP audit trails |
|
|
Cloud Data Loss Prevention API |
Classification and redaction of sensitive data |
|
|
Cloud HSM |
Service of hardware security module |
|
|
Cloud IAM |
Control service for resource access |
|
|
Cloud Identity |
Management of apps, users and devices |
|
|
Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy |
App sign-in feature based on identity |
|
|
Cloud Key Management Service |
Hosted service for key management |
|
|
Cloud Resource Manager |
Management service for cloud project metadata |
|
|
Cloud Security Scanner |
Scanner for app engine security |
|
|
Cloud Security Command Center |
Service for discovery, search, management and inventory of assets |
|
|
Context-aware Access |
Access control for end-users on the basis of attributes |
|
|
Event Threat Detection |
Scanning for anomalous activity |
|
|
Managed Service for Microsoft Active Directory |
Managed Microsoft Active Directory service |
|
|
Security Key Enforcement |
Two-phase key verification |
|
|
Shielded VMs |
Hardened VMs |
|
|
Titan Security Key |
Two-factor authentication device |
|
|
VPC Service Controls |
VPC constrain data |
|
|
Management tools |
Cloud APIs |
APIs meant for cloud services |
|
Cloud Billing |
Tools for billing and cost management |
|
|
Cloud Billing API |
Programmatic management of GCP billing |
|
|
Cloud Console |
Web-based management console |
|
|
Cloud Deployment Manager |
Deployment of infrastructure according to template |
|
|
Cloud Mobile App |
GCP manager app for iOS and Android |
|
|
Cloud Shell |
Browser-specific terminal or CLI |
|
|
Stackdriver Debugger |
Debugging in live production |
|
|
Stackdriver Error Reporting |
Reporting app errors |
|
|
Stackdriver Logging |
Centralized logging |
|
|
Stackdriver Monitoring |
Monitoring infrastructure and application |
|
|
Stackdriver Profiler |
CPU and heap profiling |
|
|
Stackdriver Transparent SLIs |
Monitoring GCP services |
|
|
Stackdriver Trace |
Insights into app performance |
|
|
Developer Tools |
Cloud SDK |
CLI for Google Cloud Platform |
|
Cloud Build |
Continuous integration or continuous delivery platform |
|
|
Cloud Code |
Cloud-native IDE extensions |
|
|
Cloud Source Repositories |
Hosted private git repos |
|
|
Cloud Scheduler |
Managed service for cron job |
|
|
Cloud Tasks |
Execution of asynchronous tasks |
|
|
Cloud Tools for IntelliJ |
Tools for IntelliJ GCP |
|
|
Cloud Tools for PowerShell |
GCP tools for PowerShell |
|
|
Cloud Tools for Visual Studio |
Tools for Visual Studio GCP |
|
|
Cloud Tools for Eclipse |
Tools for Eclipse GCP |
|
|
Container Registry |
Private container registry or storage |
|
|
Gradle App Engine Plugin |
Plugin for Gradle App Engine |
|
|
Maven App Engine Plugin |
Plugin for Maven App Engine |
|
|
Migration to Google Cloud Platform |
Cloud Data Transfer |
Tools or CLI for data migration |
|
Google Transfer Appliance |
Data transfer box available for rent |
|
|
Cloud Storage Transfer Service |
Inter-cloud transfers |
|
|
BigQuery Data Transfer Service |
Importing analytics data in bulk |
|
|
Migrate from Amazon Redshift |
Migration from Redshift to BigQuery service |
|
|
Migrate from Teradata |
Migration from Teradata to BigQuery service |
|
|
Migrate from Anthos |
Migration of VMs to GKE containers |
|
|
Migrate from Compute Engine |
Migration tools for Compute Engine |
|
|
VM Migration |
Tools for VM migration |
|
|
API Platforms |
API Analytics |
API Metrics |
|
API Monetization |
Monetization of APIs |
|
|
Apigee API Platform |
Development, security and monitoring of APIs |
|
|
Apigee Sense |
Protection of API from attacks |
|
|
Apigee Hybrid |
Management of hybrid or multi-cloud API environments |
|
|
Cloud Endpoints |
Cloud API gateway |
|
|
Cloud Healthcare API |
Interoperability of healthcare system GCP |
|
|
Developer Portal |
API management portal |
|
|
GCP Marketplace |
Partner and open-source marketplace |
|
|
GCP Foundational Open Source Projects |
Apache Beam |
Batch or streaming data processing service |
|
gRPC |
RPC (Remote Procedure Call) framework |
|
|
gVisor |
Secure container runtime |
|
|
Istio |
Connecting and securing services |
|
|
Knative |
Serverless framework for Kubernetes |
|
|
Kubeflow |
Machine Learning toolkit for Kubernetes |
|
|
Kubernetes |
Containerized application management service |
|
|
OpenCensus |
Framework for cloud native observability |
|
|
TensorFlow |
Machine Learning framework |
Google Cloud Platform Certifications
One of the crucial components of this GCP Cheat Sheet 2020 is the list of Google Cloud certifications. The certifications by Google Cloud Platform could help in gaining recognition for different skills in working on GCP. Certifications can help in validating skills in designing, development, management, and administration of application infrastructure and data solutions on GCP. The whole spectrum of Google Cloud Platform certifications involves associate-level and professional level certifications.
The only associate-level certification of GCP is the Associate Google Cloud Engineer certification. The Cloud Engineer Certification focuses on core Google Cloud Platform technology and is ideal for any beginner in GCP.
Professional certifications in GCP help in validating role-based assessment and evaluation of design and implementation skills. The list of professional-level GCP certifications is the last element before rounding up this Google cloud cheat sheet presented as follows.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Architect.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Data Engineer.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Developer.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional DevOps Engineer.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Network Engineer.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer.
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Collaboration Engineer.
Google Cloud also has another product proficiency certification known as the G Suite certification. It helps in validating the ability of the candidate for collaboration skills using core GCP tools and services.
Final Words
Based on the information in the above-mentioned Google cloud cheat sheet, any reader could get a basic idea about GCP. Google Cloud Platform is a name that resounds prolific expertise and years of experience in data center management. Furthermore, the extensive network of Google and ongoing projects for expansion imply a strong future for Google Cloud Platform.
Therefore, the transition towards a career on Google Cloud Platform can render prolific long-term benefits in terms of professional development. In addition, the appealing remuneration structures for Google Cloud certified professionals also presents clear signs for considering the significance of GCP. If you are interested in a career related to the cloud, why not Google Cloud?
Getting a Google Cloud Architect certification can help you validate and recognize your expertise on Google Cloud Platform. If you are a Google certified professional such as Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer and thinking to give your skills a recognition, check out our Google Cloud certification training courses. So, start your preparation and get ahead to become a Google Cloud Certified professional.
- Cloud DNS – A Complete Guide - December 15, 2021
- Google Compute Engine: Features and Advantages - December 14, 2021
- What is Cloud Run? - December 13, 2021
- What is Cloud Load Balancing? A Complete Guide - December 9, 2021
- What is a BigTable? - December 8, 2021
- Docker Image creation – Everything You Should Know! - November 25, 2021
- What is BigQuery? - November 19, 2021
- Docker Architecture in Detail - October 6, 2021



