With more and more applications moving to the cloud; security has become a crucial element of cloud computing. Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK) V.4 Exam Questions is globally recognized as a cloud security certification.
If you are a multi-cloud or IT professional looking for a glowing career in cloud security, the CCSK Certification Exam Questions is recommended for you.
This set of 25 CCSK certification Exam practice questions will give you a first-hand understanding of Cloud Security fundamentals. It’s based on the CCSK exam pattern.
Cloud Computing Concepts and Architectures
Q 1. Which of the following facilitates the underlying communications method for components within a cloud, some of which are exposed to the cloud user to manage their resources and configurations?
A. Cloud Service Provider
B. Cloud management plane
C. Cloud control plane
D. Application Programming Interface
E. Hypervisor
Answer: The correct answer is D.
APIs are typically the underlying communications method for components within a cloud, some of which (or an entirely different set) are exposed to the cloud user to manage their resources and configurations.
The cloud resources are pooled using abstraction and orchestration. Abstraction, often via virtualization, frees the resources from their physical constraints to enable pooling. Then a set of core connectivity and delivery tools (orchestration) ties these abstracted resources together, creates the pools, and provides the automation to deliver them to customers.
All this is facilitated using Application Programming Interfaces. APIs are typically the underlying communications method for components within a cloud, some of which (or an entirely different set) are exposed to the cloud user to manage their resources and configurations. Most cloud APIs these days use REST (Representational State Transfer), which runs over the HTTP protocol, making it extremely well suited for Internet services.
In most cases, those APIs are both remotely accessible and wrapped into a web-based user
interface. This combination is the cloud management plane since consumers use it to manage and configure the cloud resources, such as launching virtual machines (instances) or configuring virtual networks. From a security perspective, it is both the biggest difference from protecting physical infrastructure (since you can’t rely on physical access as a control)
and the top priority when designing a cloud security program. If an attacker gets into your management plane, they potentially have full remote access to your entire cloud deployment.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 2. Which layer of the logical stack includes code and message queues?
A. Infrastructure
B. Metastructure
C. Infostructure
D. Applistructure
Answer: The correct answer is D.
Applistructure: The applications deployed in the cloud and the underlying application services used to build them. For example, Platform as a Service features like message queues, artificial intelligence analysis, or notification services.
At a high level, both cloud and traditional computing adhere to a logical model that helps identify different layers based on functionality. This is useful to illustrate the differences between the different computing models themselves:
• Infrastructure: The core components of a computing system: compute, network, and storage. The foundation that everything else is built on. The moving parts.
•Metastructure: The protocols and mechanisms that provide the interface between the
infrastructure layer and the other layers. The glue that ties the technologies and enables
management and configuration.
•Infostructure: The data and information. Content in a database, file storage, etc.
•Applistructure: The applications deployed in the cloud and the underlying application services used to build them. For example, Platform as a Service features like message queues, artificial intelligence analysis, or notification services.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 3. Which of the following is a cloud infrastructure that is shared by several organizations and supports a specific group that has shared concerns?
A. Public Cloud
B. Private Cloud
C. Community Cloud
D. Hybrid Cloud
E. Common Cloud
Answer: The correct answer is C.
Community Cloud is the cloud infrastructure that is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g. mission, security requirements, policy, or compliance considerations).
Community Cloud – The cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g. mission, security requirements, policy, or compliance considerations). It may be managed by the organizations or by a third party and may be located on-premises or off-premises.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 4. Which plane is used by consumers to launch virtual machines or configure virtual networks?
A. Infrastructure Plane
B. Cloud Control Plane
C. Management Plane
D. Application Plane
E. Virtual Plane
Answer: The correct answer is C.
In most cases, those APIs are both remotely accessible and wrapped into a web-based user interface. This combination is the cloud management plane since consumers use it to manage and configure the cloud resources, such as launching virtual machines (instances) or configuring virtual networks. From a security perspective, it is both the biggest difference from protecting physical infrastructure (since you can’t rely on physical access as a control) and the top priority when designing a cloud security program.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 5. Which of the following essential characteristics of a cloud allows customers to closely match resource consumption with demand?
A. Resource Pooling
B. On-demand self-service
C. Broad network access
D. Rapid elasticity
E. Measured service
Answer: The correct answer is D
Rapid elasticity.
Rapid elasticity allows consumers to expand or contract the resources they use from the pool (provisioning and de-provisioning), often completely automatically. This allows them to more closely match resource consumption with demand (for example, adding virtual servers as demand increases, then shutting them down when demand drops).
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Governance and Enterprise Risk Management
Q 6. Which of the following is the primary tool of governance between a cloud provider and a cloud customer which is true for both public and private cloud?
A. Audit
B. Cloud provider assessment
C. Compliance Reports
D. Contract
E. Non-Disclosure Agreement
Answer: The correct answer is D.
The primary tool of governance is the contract between a cloud provider and a cloud customer (this is true for public and private cloud).
As with any other area, there are specific management tools used for cloud governance. This list focuses more on tools for external providers, but these same tools can often be used internally for private deployments:
Contracts: The primary tool of governance is the contract between a cloud provider and a
cloud customer (this is true for public and private clouds). The contract is your only guarantee
of any level of service or commitment—assuming there is no breach of contract, which tosses everything into a legal scenario. Contracts are the primary tool to extend governance into business partners and providers.
Supplier (cloud provider) Assessments: These assessments are performed by the potential cloud customer using available information and allowed processes/techniques. They combine contractual and manual research with third-party attestations (legal statements often used to communicate the results of an assessment or audit) and technical research. They are very similar to any supplier assessment and can include aspects like financial viability, history, feature offerings, third-party attestations, feedback from peers, and so on.
Q 7. Which of the following is an underlying vulnerability related to loss of Governance?
A. Lack of reputational isolation
B. Lack of resource isolation
C. Hypervisor vulnerabilities
D. Unclear asset ownership
E. Lack of supplier redundancy
Answer: The correct answer is D.
Vulnerabilities related to lack of Governance are:
- Unclear roles and responsibilities
- Poor enforcement of role definitions
- Synchronizing responsibilities or contractual obligations external to the cloud
- SLA clauses with conflicting promises to different stakeholders
- Audit or certification not available to customers
- Cross-cloud applications creating hidden dependency
- Lack of standard technologies and solutions
- Storage of data in multiple jurisdictions and lack of transparency about THIS
- No source escrow agreement
- No control on the vulnerability assessment process
- Certification schemes not adapted to cloud infrastructures
- Lack of information on jurisdictions
- Lack of completeness and transparency in terms of use
- Unclear asset ownership
Options A, B, and C are not correct as they are the vulnerabilities related to “Loss of business reputation due to co-tenant activities”.
Option E is not correct as it is a vulnerability related to “Supply Chain Failure”.
Source: enisa
Q 8. Which of the following defines the amount of risk that the leadership and stakeholders of an organization are willing to accept?
A. Risk Acceptance
B. Risk Tolerance
C. Residual Risk
D. Risk Target
Answer: The correct answer is B
Risk Tolerance.
Risk tolerance is the amount of risk that the leadership and stakeholders of an organization are willing to accept. It varies based on asset and you shouldn’t make a blanket risk decision about a particular provider; rather, assessments should align with the value and requirements of the assets involved. Just because a public cloud provider is external and a consumer might be concerned with shared infrastructure for some assets doesn’t mean it isn’t within risk tolerance for all assets. Over time this means that, practically speaking, you will build out a matrix of cloud services along with which types of assets are allowed in those services. Moving to the cloud doesn’t change your risk tolerance, it just changes how risk is managed.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 9. Which of the following can the cloud provider implement to mitigate credential compromise or theft?
Separation of roles and responsibilities
A. Automated inventory of all assets
B. Federated method of authentication
C. Hardening of virtual machines using industry standards
D. Anomaly detection
Answer: The correct answer is E.
CREDENTIAL COMPROMISE OR THEFT
- Do you provide anomaly detection (the ability to spot unusual and potentially malicious IP traffic and user or support team behavior)? For example, analysis of failed and successful logins, unusual time of day, and multiple logins, etc.
- What provisions exist in the event of the theft of a customer’s credentials (detection, revocation, evidence for actions)?
Source: enisa
Legal Issues, Contracts, and Electronic Discovery
Q 10. Which of the following reflects the claim of an individual to have certain data deleted so that third persons can no longer trace them?
A. Right to be deleted
B. Right to be erased
C. Right to non-disclosure
D. Right to be forgotten
E. Right to privacy
Answer: The correct answer is D.
The right to be forgotten “reflects the claim of an individual to have certain data deleted so that third persons can no longer trace them.”
Data Subjects’ Rights: Data subjects have rights to information regarding the processing of their data: the right to object to certain uses of their personal data; to have their data corrected or erased; to be compensated for damages suffered as a result of unlawful processing; the right to be forgotten; and the right to data portability. The existence of these rights significantly affects cloud service relationships.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 11. When entrusting a third party to process the data on its behalf, who remains responsible for the collection and processing of the data?
A. Data Processor
B. Data Controller
C. Data Analyzer
D. Data Protector
Answer: The correct answer is B.
When entrusting a third party to process data on its behalf (a data processor), a data controller remains responsible for the collection and processing of that data. The data controller is required to ensure that any such third parties take adequate technical and organizational security measures to safeguard the data.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Compliance and Audit Management
Q 12. Which of the following is a form of a compliance inheritance in which all or some of the cloud provider’s infrastructure and services undergo an audit to a compliance standard?
A. Policy Audit
B. Pass-through Audit
C. Third Party Audit
D. Compliance Audit
Answer: The correct answer is B.
Many cloud providers are certified for various regulations and industry requirements, such as PCI DSS, SOC1, SOC2, HIPAA, best practices/frameworks like CSA CCM, and global/regional regulations like the EU GDPR. These are sometimes referred to as pass-through audits. A pass-through audit is a form of compliance inheritance. In this model all or some of the cloud provider’s infrastructure and services undergo an audit to a compliance standard. The provider takes responsibility for the costs and maintenance of these certifications.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Infrastructure Security
Q 13. Which of the following is not a security benefit of Immutable workloads?
A. Security testing can be managed during image creation
B. You no longer patch running systems or worry about dependencies
C. You can enable remote logins to run workloads
D. It is much faster to roll out updated versions
E. It is easier to disable services and whitelist applications
Correct Answer: C
You can, and should, disable remote logins to running workloads (if logins are even an option). This is an operational requirement to prevent changes that aren’t consistent across the stack, which also has significant security benefits.
Auto-scaling and containers, by nature, work best when you run instances launched dynamically based on an image; those instances can be shut down when no longer needed for capacity without breaking an application stack. This is core to the elasticity of compute in the cloud. Thus, you no longer patch or make other changes to a running workload, since that wouldn’t change the image, and, thus, new instances would be out of sync with whatever manual changes you make on whatever is running. We call these virtual machines immutable.
Immutable workloads enable significant security benefits:
· You no longer patch running systems or worry about dependencies, broken patch processes, etc. You replace them with a new gold master.
• You can, and should, disable remote logins to running workloads (if logins are even an option). This is an operational requirement to prevent changes that aren’t consistent across the stack, which also has significant security benefits.
• It is much faster to roll out updated versions since applications must be designed to handle individual nodes going down (remember, this is fundamental to any auto-scaling). You are less constrained by the complexity and fragility of patching a running system. Even if something breaks, you just replace it.
• It is easier to disable services and whitelist applications/processes since the instance should never change.
• Most security testing can be managed during image creation, reducing the need for vulnerability assessment on running workloads since their behavior should be completely known at the time of creation. This doesn’t eliminate all security testing for production workloads, but it is a means of offloading large portions of testing
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4
Q 14. Which of the following leverages virtual network topologies to run smaller, and more isolated networks without incurring additional hardware costs?
A. Microsegmentation
B. VLANs
C. Converged networking
D. Virtual Private Networks
E. Virtual Private Cloud
Answer: The correct answer is A,
microsegmention.
Microsegmentation (also sometimes referred to as hyper segregation) leverages virtual network topologies to run more, smaller, and more isolated networks without incurring additional hardware costs that historically make such models prohibitive. Since the entire networks are defined in software without many of the traditional addressing issues, it is far more feasible to run these multiple, software-defined environments.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 15. Installing traditional agents designed for physical servers will not result in the same amount of efficiency and performance on a virtualized server.
A. True
B. False
Answer: The correct answer is A.
“Traditional” agents may impede performance more heavily in the cloud. Lightweight agents with lower compute requirements allow better workload distribution and efficient use of resources. Agents not designed for cloud computing may assume underlying compute capacity that isn’t aligned with how the cloud deployment is designed. The developers on a given project might assume they are running a fleet of lightweight, single-purpose virtual machines. A security agent not attuned to this environment could significantly increase processing overhead, requiring larger virtual machine types and increasing costs
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Virtualization and Containers
Q 16. Which of the following are the primary security responsibilities of the cloud provider in compute virtualization? (Select 2)
A. Isolation
B. Identity & Access Management
C. Encryption
D. Securing the underlying infrastructure
E. Monitoring and Logging
Answer: The correct answer is A, D.
The primary security responsibilities of the cloud provider in compute virtualization are to enforce isolation and maintain a secure virtualization infrastructure.
Cloud Provider Responsibilities
The primary security responsibilities of the cloud provider in compute virtualization are to enforce isolation and maintain a secure virtualization infrastructure.
• Isolation ensures that compute processes or memory in one virtual machine/container should not be visible to another. It is how we separate different tenants, even when they are running processes on the same physical hardware.
• The cloud provider is also responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure and the virtualization technology from external attack or internal misuse. This means using patched and up-to-date hypervisors that are properly configured and supported with processes to keep them up to date and secure over time. The inability to patch hypervisors across a cloud deployment could create a fundamentally insecure cloud when a new vulnerability in the technology is discovered.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4
Q 17. Which of the following WAN virtualization technology is used to create networks which span multiple base networks?
A. Cloud overlay networks
B. Virtual private networks
C. Virtual private cloud
D. Network peering
Answer: The correct answer is A.
Cloud overlay networks are a special kind of WAN virtualization technology for creating networks that span multiple “base” networks. For example, an overlay network could span physical and cloud locations or multiple cloud networks, perhaps even on different providers.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 18. The most fundamental security control for any multitenant network is-
A. Hypervisor security
B. Segregation and isolation of network traffic
C. Logging and monitoring controls
D. Secure image creation process
Answer: The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
The cloud provider is primarily responsible for building secure network infrastructure and configuring it properly. The absolute top security priority is segregation and isolation of network traffic to prevent tenants from viewing another’s traffic. This is the most foundational security control for any multi-tenant network.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing
Topic: Cloud Provider Responsibilities
Domain 8 // VIRTUALIZATION AND CONTAINERS
Incident Response
Q 19. What must the monitoring scope cover in addition to the deployed assets?
A. The data plane
B. The application plane
C. The service plane
D. The access plane
E. The management plane
Answer: The correct answer is E.
In all cases, the monitoring scope must cover the cloud’s management plane, not merely the deployed assets.
Detection and analysis in a cloud environment may look nearly the same (for IaaS) and quite different (for SaaS). In all cases, the monitoring scope must cover the cloud’s management plane, not merely the deployed assets.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 20. Resource pooling practiced by the cloud services may especially complicate which part of the IR process?
A. Detection
B. Prevention
C. Monitoring
D. Recovery
E. Forensics
Answer: The correct answer is E
Forensics.
The resource pooling practiced by cloud services, in addition to the rapid elasticity offered by cloud infrastructures, may dramatically complicate the IR process, especially the forensic activities carried out as part of the incident analysis. Forensics has to be carried out in a highly dynamic environment, which challenges basic forensic necessities [4] such as establishing the scope of an incident, the collection, and attribution of data, preserving the semantic integrity of that data, and maintaining the stability of evidence overall. These problems are exacerbated when cloud customers attempt to carry out forensic activities since they operate in a non-transparent environment (which underscores the necessity of support by the cloud provider as mentioned above).
Source: Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing
Application Security
Q 21. In which of the five main phases of secure application design and development, you perform Threat Modelling?
A. Training
B. Define
C. Design
D. Develop
E. Test
Answer: The correct answer is C.
It is during the design phase that you perform threat modeling, which must also be cloud and provider/platform-specific.
Design: During the application design process, especially when PaaS is involved, the focus for security in the cloud is on architecture, the cloud provider’s baseline capabilities, cloud provider features, and automating and managing security for deployment and operations. We find that there are often significant security benefits to integrating security into the application architecture since there are opportunities to leverage the provider’s own security capabilities. For example, inserting a serverless load balancer or message queue could completely block certain network attack paths. This is also where you perform threat modeling, which must also be cloud and provider / platform-specific.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Data Security and Encryption
Q 22. Which of the following will not help to detect actual migrations, monitor cloud usage, and any data transfers to the cloud?
A. CASB – Cloud Access and Security Brokers
B. URL Filtering
C. DLP- Data Loss Prevention
D. Data Encryption in transit
Answer: The correct answer is D.
You can detect actual migrations, monitor cloud usage and any data transfers using CASB, URL filtering, and DLP. Data encryption in transit will help to secure the data while in motion but will not help to detect actual migrations, monitor cloud usage and any data transfers to the cloud
To detect actual migrations, monitor cloud usage, and any data transfers. You can do this with the help of the following tools:
CASB: Cloud Access and Security Brokers (also known as Cloud Security Gateways) discover internal use of cloud services using various mechanisms such as network monitoring, integrating with an existing network gateway or monitoring tool, or even by monitoring DNS queries. After discovering which services your users are connecting to, most of these products then offer monitoring of activity on approved services through API connections (when available) or inline interception (man in the middle monitoring). Many support DLP and other security alerting and even offer controls to better manage the use of sensitive data in cloud services (SaaS/PaaS/and IaaS).
URL filtering: While not as robust as CASB a URL filter/web gateway may help you understand which cloud services your users are using (or trying to use).
DLP: If you monitor web traffic (and look inside SSL connections) a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tool may also help detect data migrations to cloud services. However, some cloud SDKs and APIs may encrypt portions of data and traffic that DLP tools can’t unravel, and thus they won’t be able to understand the payload.
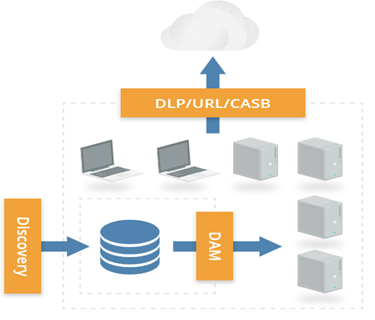
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 23. Which of the following should be the main consideration for key management?
A. Performance, access control, latency, non-repudiation
B. Performance, accessibility, latency, security
C. Performance, access control, speed,non-repudiation
D. Performance, availability, speed, security
Answer: The correct answer is B.
The main considerations for key management are performance, accessibility, latency, and security.
Key Management (Including Customer-Managed Keys)
The main considerations for key management are performance, accessibility, latency, and security. Can you get the right key to the right place at the right time while also meeting your security and compliance requirements?
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Identity, Entitlement, and Access Management
Q 24. Identity brokers handle federating between identity providers and relying parties
A. True
B. False
Answer: The correct answer is A.
Identity brokers handle federating between identity providers and relying parties (which may not always be a cloud service).
Explanation:
Identity brokers handle federating between identity providers and relying parties (which may not always be a cloud service). They can be located on the network edge or even in the cloud in order to enable web-SSO.
Identity providers don’t need to be located only on-premises; many cloud providers now support cloud-based directory servers that support federation internally and with other cloud services. For example, more complex architectures can synchronize or federate a portion of an organization’s identities for an internal directory through an identity broker and then to a cloud-hosted directory, which then serves as an identity provider for other federated connections.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Q 25. Which of the following is a preferred model for cloud-based access management?
A. Role based
B. Identity based
C. Access Based
D. Attribute based
Answer: The correct answer is D.
• ABAC is the preferred model for cloud-based access management.
Cloud platforms tend to have greater support for the Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) model for IAM, which offers greater flexibility and security than the Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) model.
RBAC is the traditional model for enforcing authorizations and relies on what is often a single attribute (a defined role). ABAC allows more granular and context-aware decisions by incorporating multiple attributes, such as role, location, authentication method, and more.
Source: Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing V4.0
Conclusion:
Cloud Security is a complex domain, especially in a multi-cloud environment. The above set of 25 CCSK Exam practice questions are based on Cloud Security fundamentals. This should give you a glimpse of the CCSK exam pattern and also make you familiar with the CCSK Exam questions format.
When are you planning to take the CCSK exam? We recommend you practice more in an actual exam environment.
Reference Links:
- 25 Free Questions – Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge V.4 - December 13, 2021
- 25 Free Questions on PL-900 Exam Certification - December 3, 2021
- 50 Free Terraform Certification Exam Questions - December 2, 2021
- 25 Free Questions – GCP Certified Professional Cloud Network Engineer - December 2, 2021
- 25 Free Questions – Microsoft Power BI PL-300 (DA-100) Certification - December 2, 2021
- 25 Free Questions – Google Cloud Developer Certification Exam - November 30, 2021
- 25 Free Questions – Google Cloud Certified Professional Security Engineer - November 30, 2021
- 25 Free Questions – Google Cloud Certified Professional Machine Learning Engineer - November 30, 2021



