The Azure storage solution is Azure cloud-based and it allows the end users to store, access, and process the data-based objects in the cloud environment.
By leveraging the Azure storage solution, you can achieve high scalability, durability, and availability while accessing the Azure-based storage services and applications.
Azure blob storage service is employed for managing workloads that need high-capacity storage. Azure data lake storage service is meant for managing big data analytics workloads.
In this blog article, you will learn the distinctions between the Azure blob storage vs data lake in detail. This article is designed to assist readers in preparing for the Azure Administrator Associate certification and to provide a comprehensive understanding of Azure Data storage types.
Without further ado, let’s dive in!
Azure Blob Storage vs Data Lake: Key Definitions
Azure blob storage
Azure blob storage is object-based cloud storage, that handles both unstructured and semi-structured data. In this storage solution, the blobs are converted into containers like folders in the file system and accessed through REST API, Azure Powershell, CLI, and client libraries.
It offers varied storage tiers to maintain the performance and cost needs such as hot, archive, and cool tiers, which may differ in accessing and availability timings. And offers varied storage options for varied data types such as files, queues, and blobs.
In addition, blob storage offers some distinct features such as lifecycle management, versioning, and data lake storage Gen2 integration. It serves as a versatile object store for unstructured data within a flat namespace and single hierarchy.
Common applications of Azure Blob Storage include storing files for distributed access, streaming video and audio, archiving backups for disaster recovery, and managing binary data like application back-end files.
It is optimized in such a way as to handle the storage and retrieval of large-sized files such as images, backups, and videos and offers access to the retained data through HTTP.
Azure Data Lake
The Azure Data Lake platform supports big data analytics, offers unlimited storage for structured, semi-structured, or unstructured data, and retains any data type of any size.
It’s generally built on Azure Blob storage and it furnishes unique features such as low-cost, tiered storage and high-availability, disaster recovery capabilities, and integrates easily with other Azure services such as Azure Data Factory, which is a tool for creating and managing the extract, transform and load (ETL) processes.
The resolution relies on the Apache Hadoop YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) cluster management platform. It scales across SQL servers in the data lake and servers present in Azure SQL Database as well as Azure SQL Data Warehouse.
Azure Data Lake storage is divided into Gen1 and Gen2 options, with Microsoft retiring Gen1 in February 2024. Azure Data Lake Gen1 is designed for big data analytics workloads, featuring a hierarchical file system capable of storing machine learning data and supporting interactive streaming analytics. It is optimized for large-scale analytics systems demanding substantial throughput and bandwidth for querying and analyzing extensive datasets.
On the other hand, Azure Data Lake Gen2 combines the functionalities of Gen1 with Blob Storage, inheriting Gen1’s file system semantics, file-level security, and scaling features while building on the foundation of Blob Storage. This integration results in a cost-effective, tiered-access, highly secure, and highly available big data storage solution.
Azure blob storage vs data lake: Features
Here’s a simplified overview of Azure blob storage vs data lake features:
Features of Azure blob storage
The key features of Azure blob storage such as:
- This system allows you to store unstructured data in blobs to accommodate various data types like text, binary data, images, videos, and other files.
- Data is redundantly stored in multiple locations, ensuring both high availability and data redundancy.
- This platform features scalability, enabling the storage and retrieval of an unlimited amount of data without constraints.
- Security measures, including encryption, role-based access control, and shared access signatures, are incorporated to guarantee the protection of your data.
- Additionally, different access tiers, such as hot, cool, and archive tiers, are offered to assist in cost management based on the frequency of data access.
Features of Data Lake
Here are some of the key features and benefits of using Azure Data Lake:
- Simplified data management: With Azure Data Lake, you can eliminate the hurdles of handling multiple data storage systems by using a single and unified platform for all of the different data types.
- Improved data accessibility: You can easily get the data and process it with Azure Data Lake to gain valuable insights and make effective data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced data security: Robust security features of the Azure Data Lake can protect your sensitive data to ensure your data complies with industry standards and regulations.
- Cost-effective scalability: As data storage and processing occurs daily, Azure Data Lake can manage it by scaling out those data at low cost and eliminating on-premises infrastructure complexities.
- Accelerated innovation: You can achieve advanced analytics by employing Azure Data Lake, machine learning, and real-time processing, your firm can develop and deploy innovative applications and services efficiently.
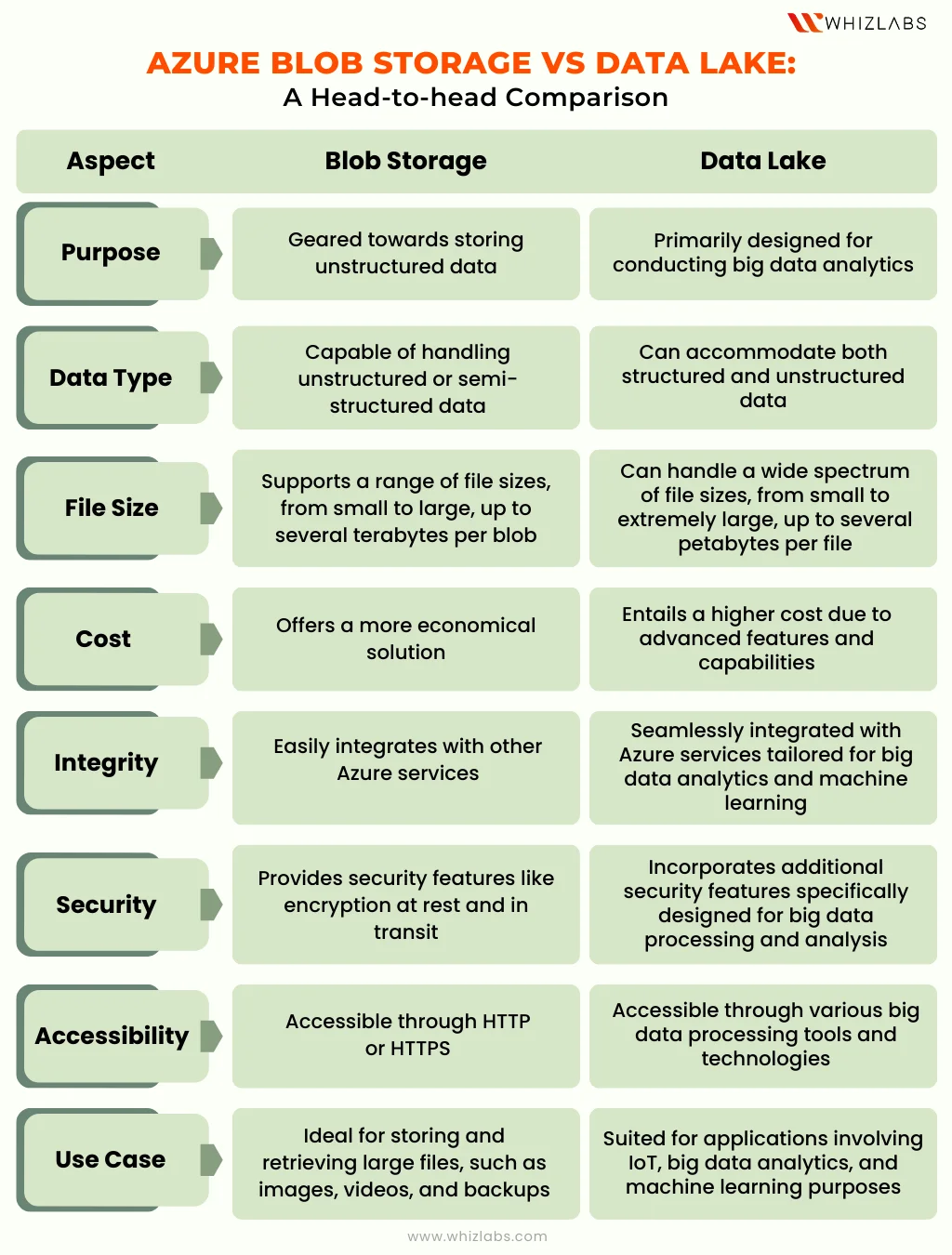
Azure Blob Storage vs Data Lake: A Head-to-head Comparison
Azure Blob Storage excels in handling unstructured data efficiently, making it suitable for serving images or documents directly to browsers and storing files intended for distributed access. On the other hand, Azure Data Lake is engineered for robust big data analytics, accommodating the storage and analysis of vast amounts of data.
Let’s see more distinctions lie between them:
By the end of this analysis, you’ll be equipped with insights to navigate the decision-making process and determine which Azure storage solution aligns best with your specific requirements.
Azure blob storage vs Azure Data lake: Which one is better?
Choosing between Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake solely depends on specific use cases and requirements. Each Azure storage service has its strengths and is optimized based on different scenarios.
In a nutshell, Azure Blob Storage is suited for general-purpose object storage. It is highly scalable and can handle varied data types, including unstructured data, documents, images, and videos. Blob Storage is cost-effective and is often used for applications like backup, archiving, and serving static assets for web applications.
On the other hand, Azure Data Lake Storage is designed for big data analytics. It is optimized for handling large amounts of data, especially for analytics and processing tasks.
Data Lake Storage supports hierarchical file systems, making it easier to organize and manage data in a way that aligns with the structure of the data itself. It is an excellent choice for scenarios involving large-scale analytics, machine learning, and data warehousing.
If your primary needs involve general-purpose object storage and versatility, Azure Blob Storage may be the better choice.
If you are dealing with big data analytics and complex data processing, and require a hierarchical file system, Azure Data Lake Storage might be more suitable.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific requirements and objectives of your project.
Also Read : Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer – What are the storage options available in Microsoft Azure?
Azure Blob vs Data Lake Storage: Benefits & Challenges
Azure Blobs provides a robust storage solution with appropriate redundancy options to ensure data durability. All data is encrypted, and fine-grained access control is available. Azure Blobs are highly scalable, making them suitable for storing both text and binary data.
While Azure Blob Storage and Data Lake are well-suited for specific use cases, a challenge with Azure Blobs is the potential for high data transfer charges.
These charges include typical read/write charges at different tiers (Premium, Hot, Cool, and Archive), as well as additional costs for iterative read/write operations, indexing, SSH FTP transfers, fees for geo-replicated data transfers, and more.
Although individual transfer costs may be small, they can accumulate significantly when dealing with a large number of transactions.
Azure Data Lake, on the other hand, facilitates the storage and analysis of petabytes of data quickly and efficiently. It centralizes data storage, ensures encryption for all data, and provides role-based access control.
Due to its high customizability, Azure Data Lake storage is cost-effective. Users can independently scale storage and computing services and optimize costs through object-level tiering.
Azure Blob vs. Data Lake Storage: Pricing
Azure Blob Storage and Data Lake follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model, determined by factors such as the monthly volume of stored data, the types and quantity of operations performed, and the chosen data redundancy options.
For users with stable storage needs or those accessing archives and backups infrequently, there is an option to opt for Reserved Capacity, available in increments of 100 TB and 1 PB for commitments of one or three years.
Blob Storage pricing is tiered, with options like Premium, Hot, Cool, and Archive. The Premium tier is suitable for I/O-intensive workloads requiring low and consistent storage latency.
Storage pricing ascends from Archive to Cool to Hot to Premium, while transaction pricing follows the opposite progression – for instance, Archive transactions are more expensive than Premium transactions.
For organizations utilizing multiple Azure products and services, leveraging the Azure pricing calculator is recommended to ensure optimal and cost-effective pricing.
FAQs
How many types of blob storage are available in Azure?
There are three blobs of storage available in the Azure cloud platform.
What is the storage limit of Azure data lake?
Azure Data Lake can store trillions of files, and a single file storage can exceed a petabyte size. This is 200 times larger than what is typically supported by other cloud storage solutions. The advantage of this large file size support is that you won’t need to rewrite code when scaling up or down the size of stored data or the compute resources being utilized. This flexibility allows for seamless adjustments without the need for extensive code modifications.
What are the components of Azure Data Lake?
Azure Data Lake comprises three main components such as storage, analytics service, and cluster capabilities.
Why use Blob storage?
Blob Storage is designed for efficiently storing extensive quantities of unstructured data, including text or binary data. It is well-suited for tasks such as directly delivering images or documents to a web browser and storing files intended for distributed access.
What type of storage is Blob Storage?
Blob storage is a category of cloud storage specifically designed for unstructured data. A “blob,” abbreviated for Binary Large Object, refers to a substantial amount of data in binary form that may not adhere to any predefined file format.
Conclusion
Hope this blog provides a detailed comparison of Azure blob storage vs data lake.
By understanding the nuances and strengths of this storage service, AZ-104 certification takers can make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their projects.
To level up preparation to the next level, just give a try on Azure hands-on labs and Azure sandboxes. These real-time settings hone your practical skills in managing the issues that arise in Azure storage.
- Top 25 AWS Data Engineer Interview Questions and Answers - May 11, 2024
- What is Azure Synapse Analytics? - April 26, 2024
- AZ-900: Azure Fundamentals Certification Exam Updates - April 26, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Data Engineer Associate Certification - April 19, 2024
- Maximizing Cloud Security with AWS Identity and Access Management - April 18, 2024
- A Deep Dive into Google Cloud Database Options - April 16, 2024
- GCP Cloud Engineer vs GCP Cloud Architect: What’s the Difference? - March 22, 2024
- 7 Ways to Double Your Cloud Solutions Architect Role Salary in 12 Months - March 7, 2024