Are you preparing for the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate certification exam? Are you ready to pass this exam? In this blog, we are writing a series of articles on topics that are covered in the AWS Certified SysOps associate certification exam. You can subscribe to us to receive further updates on this topic.
The SysOps Associate certification exam is the hardest exam at the associate certification level. We would recommend you pass both the solution architect-associated certification exam and developer-associated certification exam first before of taking this exam.
The AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate exam validates technical expertise in deployment, management, and operations on the AWS platform
The AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate Level exam validates the candidate’s ability to:
- Deliver the stability and scalability needed by a business on AWS
- Provision systems, services, and deployment automation on AWS
- Ensure data integrity and data security on AWS technology
- Provide guidance on AWS best practices
- Understand and monitor metrics on AWS
Figure #0. Domains covered by the AWS Certified SysOps associate exam
You can download the related AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate Level Exam Blueprint for more detail about it.
In this article, we are going to explain the topic that addresses the understanding of the shared responsibility model as highlighted in the AWS Blueprint from the above exam guide.
Context
Cloud security at AWS is the highest priority. As an AWS customer, you will benefit from a data center and network architecture built to meet the requirements of the most security-sensitive organizations. Access to your AWS resources should be following always the least privilege. It will warrant better integrity, confidentiality, and availability of your AWS resources and data/information.
Amazon Web Services Cloud Compliance enables customers to understand the robust controls in place at AWS to maintain security and data protection in the cloud. As systems are built on top of AWS cloud infrastructure, compliance responsibilities will be shared.
The Security of a Cloud Solution
When evaluating the security of a cloud solution, it is important for customers to understand and distinguish between:
|
Concept |
Brief description |
| Security of the cloud | This kind of Security measures that the cloud service provider (AWS) implements and operates. It is managed by Amazon AWS. |
| Security in the cloud | This kind of Security measures that the customer implements and operates, related to the security of customer content and applications that make use of AWS services. It is the responsibility of the customer. |
In this scenario, the customers retain control of what security they choose to implement to protect their own information and infrastructure, no differently than they today are doing in their on-premise infrastructure.
When you decide to move your IT infrastructure to AWS services, it immediately creates a model of shared responsibility between your company as a customer and AWS.
Are you an AWS Security professional? AWS Security Specialty certification recognizes and demonstrates your knowledge of AWS security. Plan now to validate your skills with the AWS Certified Security Speciality exam!
The Shared Responsibility Model
While AWS manages the security of the cloud, security in the cloud is the responsibility of the customer. Customers retain control of what security they choose to implement to protect their own content, platform, applications, systems, and networks.
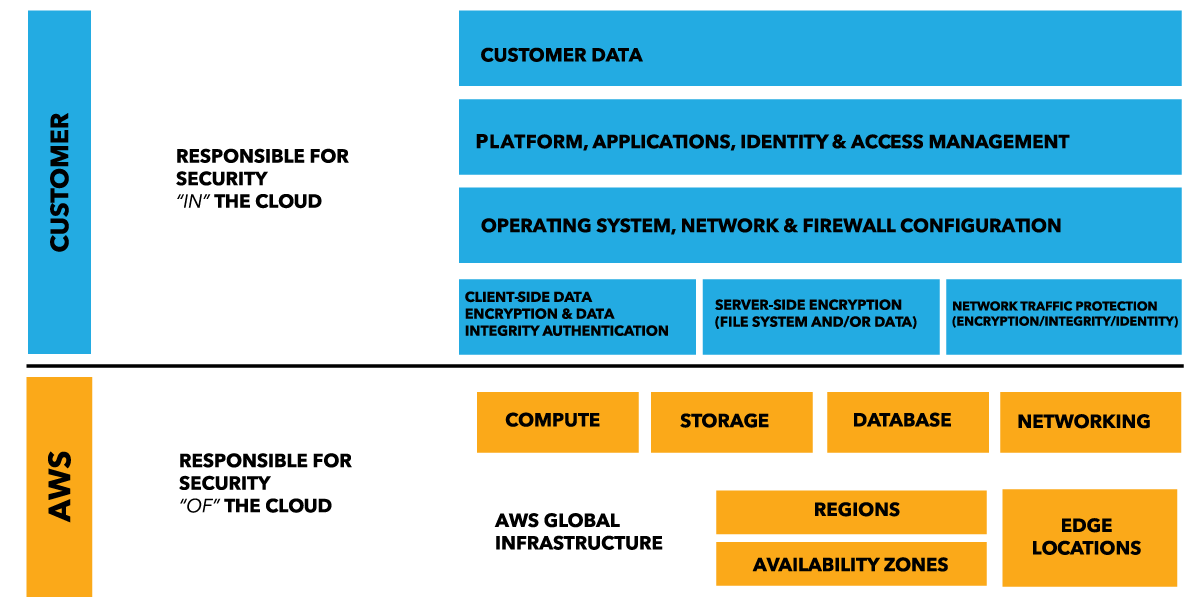
Figure #1. The Shared Responsibility Model
As you see, the customer is responsible by:
- The authentication, authorization, integrity, and encryption of the client-side data
- The encryption of server-side information via file system or directly into the data storage
- The protection of the flow of information through the network warranties your identity, integrity, and encryption in the transportation
- Assuming the responsibility and management of the guest operating system including updates patches and other associated software
- Securing the configuration related to the network and networking devices configuration like firewall, using securing controls like NACLs (network access control lists) and security groups
- Deploying, configuring, and deploying security baselines within their AWS available services
In summary, the customer assumes responsibility and management of the guest operating system (including updates and security patches), other associated application software, as well as the configuration of the AWS-provided security group firewall. All AWS customers retain ownership and control of their data.
Finally, the AWS provider is responsible by:
- Protecting the global infrastructure for services that run in the cloud
- The physical infrastructure and facilities in which the service operates, where running the AWS resources of the customer
- The access control and protection from external attacks on the physical AWS services and resources
- Operating, managing, and controlling the components from the host operating system and virtualization layer
In summary, AWS operates, manages, and controls the components from the host operating system and virtualization layer down to the physical security of the facilities in which the service operates. AWS simply makes available the computing, storage, database, and networking services selected by the customer.
Customers should carefully consider the services they choose as their responsibilities vary depending on the services used, the integration of those services into their IT environment, and applicable laws and regulations.
It is possible for customers to enhance security and/or meet their more stringent compliance requirements by leveraging technology such as host-based firewalls, host-based intrusion detection/prevention, encryption and key management. The nature of this shared responsibility also provides the flexibility and customer control that permits the deployment of solutions that meet industry-specific certification requirements.
This customer/AWS shared responsibility model also extends to IT controls. Just as the responsibility to operate the IT environment is shared between AWS and its customers, so is the management, operation, and verification of IT controls shared.
Customers can then use the AWS control and compliance documentation available to them to perform their control evaluation and verification procedures as required.
AWS Compliance best practices
The AWS control environment is subject to regular internal and external risk assessments. AWS engages with external certifying bodies and independent auditors to review and test the AWS overall control environment.
AWS does communicate its security and control environment relevant to customers. AWS does this by doing the following:
- Obtaining industry certifications and independent third-party attestations described in the AWS Compliance Whitepaper
- Publishing information about the AWS security and control practices in whitepapers and website content
- Providing certificates, reports, and other documentation directly to AWS customers under NDA (as required)
AWS strictly controls access to data centers, even for internal employees. Third parties are not provided access to AWS data centers except when explicitly approved by the appropriate AWS data center manager per the AWS access policy. Controls in place limit access to systems and data and provide that access to systems or data is restricted and monitored. In addition, customer data is and server instances are logically isolated from other customers by default.
The AWS environment is a virtualized, multi-tenant environment. AWS has implemented security management processes, PCI controls, and other security controls designed to isolate each customer from other customers. AWS systems are designed to prevent customers from accessing physical hosts or instances not assigned to them by filtering through the virtualization software.
Important Points to Remember for the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate Certification exam
- AWS Compliance enablers to help customers establish and operate in an AWS security control environment
- The shared responsibility model is part of the AWS Compliance program
- The Security of the cloud is managed by Amazon AWS provider
- Security in the cloud is responsibility of the customer
- The customer is responsible for their information and data, their secure transmission, integrity, and encryption
- Also, the customer is responsible for managing, supporting, patching, and control of the guest operating system and AWS services provided like EC2
- AWS customers retain control and ownership of their data
- The AWS network provides significant protection against traditional network security issues and the customer can implement further protection
Summary
In this article, we have explained the shared responsibility model as part of the compliance management of AWS services, where there are specific responsibilities delegated to the customer and AWS provider.
References:
[1] Compliance: The shared responsibility model. Amazon AWS. https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/shared-responsibility-model/
[2] AWS Risk and Compliance Overview. Amazon AWS whitepaper. https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/compliance/AWS_Risk_and_Compliance_Overview.pdf
[3] AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate Certification.https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-sysops-admin-associate/
- Top 20 Questions To Prepare For Certified Kubernetes Administrator Exam - August 16, 2024
- 10 AWS Services to Master for the AWS Developer Associate Exam - August 14, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Machine Learning Specialty Certification - August 7, 2024
- Best 15+ AWS Developer Associate hands-on labs in 2024 - July 24, 2024
- Containers vs Virtual Machines: Differences You Should Know - June 24, 2024
- Databricks Launched World’s Most Capable Large Language Model (LLM) - April 26, 2024
- What are the storage options available in Microsoft Azure? - March 14, 2024
- User’s Guide to Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine - March 1, 2024


