Are you preparing for AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional certification exam? In this space, we are writing a series of articles on topics which are covered in the Solutions Architect Professional certification exam. In this article, we are explaining one of the important services offered by Amazon web services, which is AWS CloudFront. You can subscribe to our blog for receiving the further updates on this topic.
- Try Now: AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional – Free Test
- Also Read: How to prepare for AWS certified solutions architect professional exam?
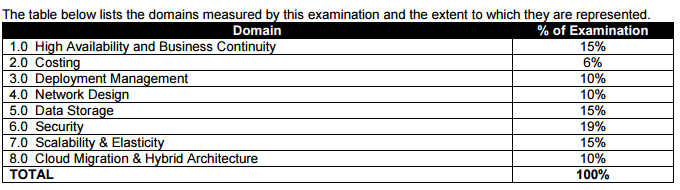
This topic addresses the High Availability and Business Continuity topic mentioned in the below table and as highlighted in the AWS Solutions Architect Professional certification exam blueprint:
What is AWS CloudFront?
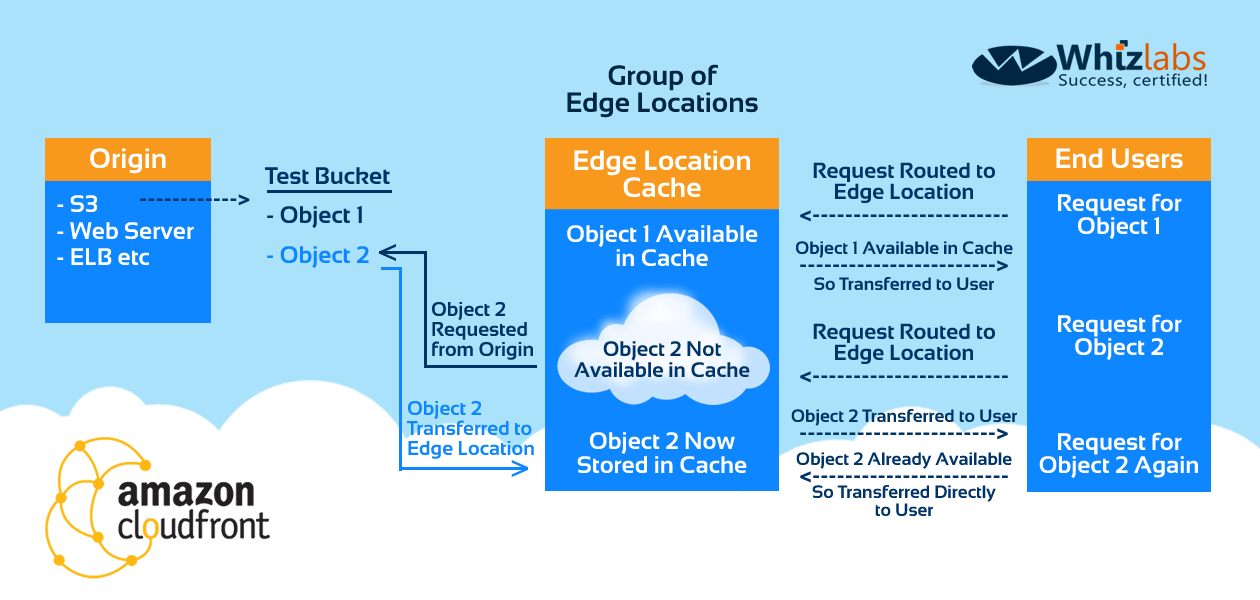
AWS CloudFront is used as a content delivery service in order to deliver content to the users around the globe via edge locations. Let’s go through some of the core terms of CloudFront.
- Origin Server – This is used to store the original versions of your files on one or more origin servers. An origin server is the location of the definitive version of an object. Origin servers could be other Amazon Web Services – an Amazon S3 bucket, an Amazon EC2 instance, or an Elastic Load Balancer. You can also have your own custom origin for CloudFront.
- Distribution – This is the CloudFront aspect which is used to route requests from the user to the edge location to the origin server. There are two types of distributions you can create – web distributions for HTTP/HTTPS and RTMP Distributions for RTMP and its variants
- Edge Cache – These are points which are located across the globe to reduce the time taken to deliver content to the end users. These caches can be used to hold the recently requested data. If the data is not available at the edge location, it will be requested from the origin server.
- TTL – Amazon CloudFront lets you configure a Minimum time-to-live (Min TTL), a Maximum TTL (Max TTL) and a Default TTL to specify how long CloudFront caches your objects in edge locations
- Query String parameters – Query string parameters are often used to return customized content generated by a script running on the origin server
Dynamic Content
AWS CloudFront can also be used to deliver dynamic content. Some of the key aspects while delivering dynamic content are given below:
- Low TTL’s – Amazon CloudFront uses the expiration period you set on your files (through cache control headers) to determine whether it needs to check the origin for an updated version of the file. If you expect that your files will change frequently, you can set a short expiration period on the file. Amazon CloudFront accepts expiration period as short as 0 seconds.
- Query String parameters – Query string parameters are often used to return customized content generated by a script running on the origin server. You can optionally configure query strings to be forwarded to the origin servers and be included in the unique identity of the cached object.
- Forward headers to the origin – You can use Amazon CloudFront to forward all (or a whitelist of) request headers to your origin server. These headers contain information such as the device used by your visitors or the country from which they accessed your content.
- Protocol detection – You can configure Amazon CloudFront to include the protocol (HTTP vs HTTPS) of your end user’s request as part of the cache key to uniquely identify an object in the cache
- HTTP Cookies – Amazon CloudFront supports delivery of dynamic content that is customized or personalized using HTTP cookies.
Creating a CloudFront Distribution
Let’s now go through the steps which can be used to create a CloudFront distribution
Step 1: Log in to the AWS console. The first step is to create an origin. Let’s create the origin as an S3 bucket. So, let’s go over to the S3 section first.
Step 2: Next, let’s create a bucket. Click on Create bucket.
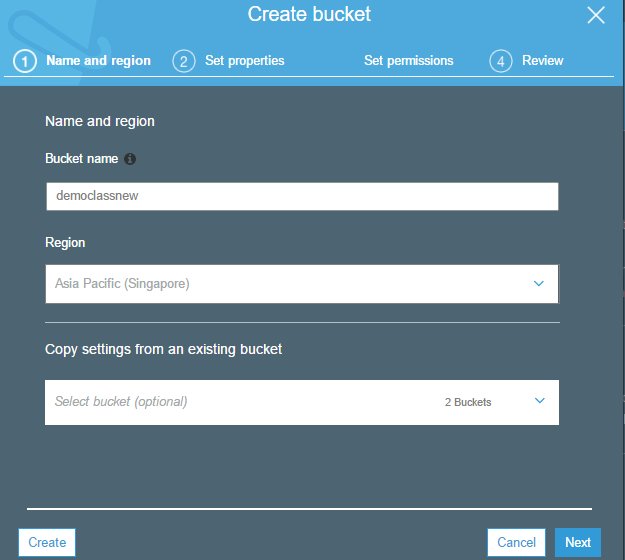
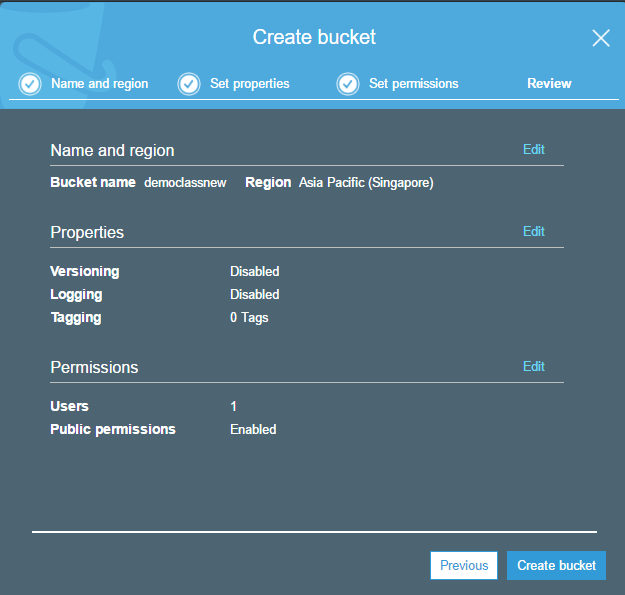
Step 3: Give a name for the bucket and specify the region. Click on the Next button.
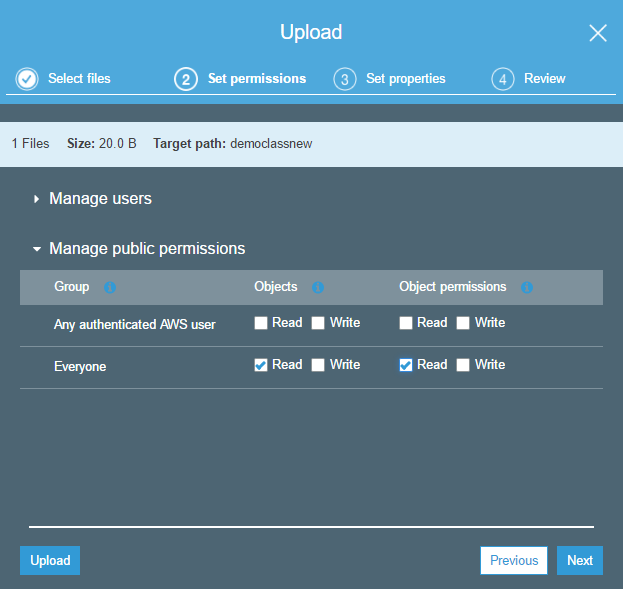
Step 4: Next when you reach the ‘Set Permissions’ page, ensure that the ‘Everyone’ entity has the Read permission.
Finally, you can click on the ‘Create button’ at the bottom of the screen.
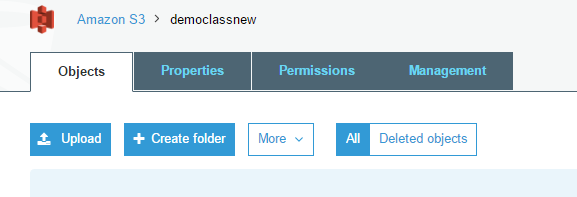
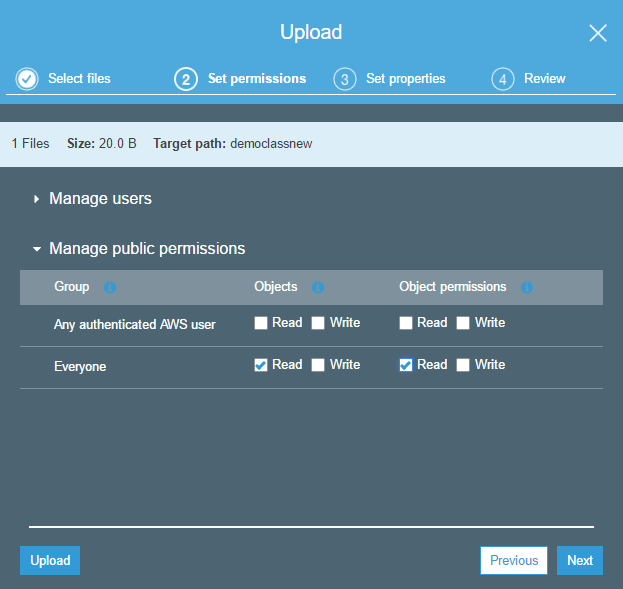
Step 5: Next let’s upload an object to the S3 bucket. Go into the bucket and click on the ‘Upload’ button.
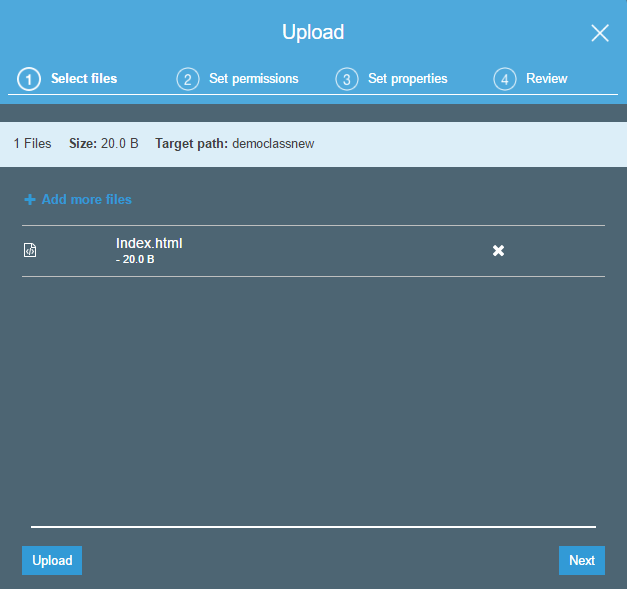
Add any simple file to the ‘Upload’ section.
Click on the Next button.
In the permission section, ensure that the ‘Everyone’ entity has the Read permission. Then finally click on the Upload button to upload the object.
Step 6: Now let’s create out the CloudFront distribution. In the AWS console, go to Networking & Content Delivery -> Cloudfront
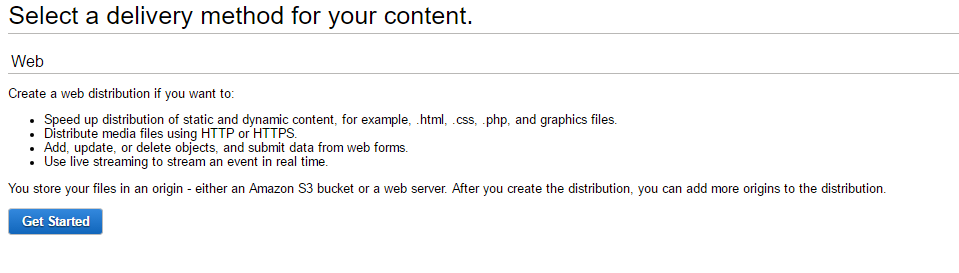
Step 7: Next click on ‘Create Distribution’
Choose the Web distribution
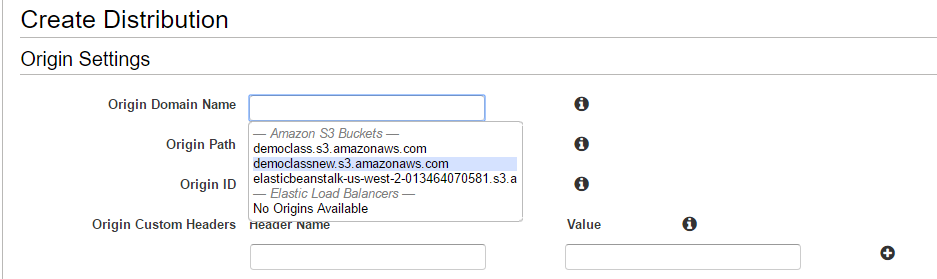
Choose the Origin domain name as the democlassnew bucket which was created in the earlier step in the next screen.
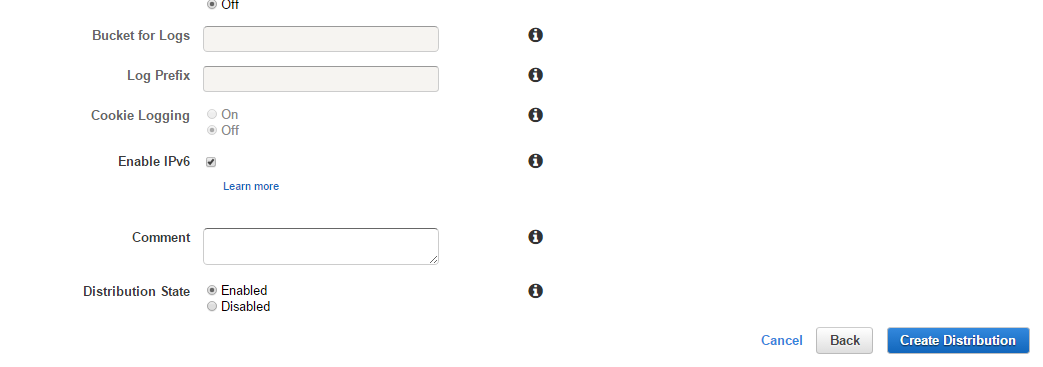
You can keep the rest of the settings as they are and click on the Create Distribution button at the bottom of the screen.
Once the distribution has been created, you will get the details of the distribution. Use the domain name to browse to the distribution.
Important Points to Remember about Cloudfront
Some important points you need to remember about Cloudfront are given below:
- Amazon CloudFront edge locations can look at the value of the User-Agent header to detect the device type of all the incoming requests. Amazon CloudFront can determine whether the end user request came from a Desktop, Tablet, Smart TV, or Mobile device and pass that information in the form of new HTTP Headers to your origin server.
- Amazon CloudFront can also detect the country from where the end users are accessing your content. Amazon CloudFront can then pass the information about the country in a new HTTP header to your custom origin server.
- You can use Amazon CloudFront’s private content feature to control who is able to access your content. This optional feature lets you use Amazon CloudFront to deliver valuable content that you prefer not to make publicly available by requiring your users to use a signed URL or have a signed HTTP cookie when requesting your content.
- CloudFront can have a custom SSL attached. Custom SSL certificate support lets you deliver content over HTTPS using your own domain name and your own SSL certificate.
- Amazon CloudFront lets you configure a Minimum time-to-live (Min TTL), a Maximum TTL (Max TTL) and a Default TTL to specify how long CloudFront caches your objects in edge locations.
- Query string parameters are often used to return customized content generated by a script running on the origin server
Don’t MISS IT: AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional – Practice Tests(50% Discount)
Bottom Line
In this article, we have explained about AWS CloudFront. AWS CloudFront is used to deliver content to users around the globe via edge locations. So, it is one of the important service provided by the Amazon Web Services (AWS). You will get a number of questions on this topic in your certification exam.
If you are preparing for the AWS certifications exam and looking for any help, put your question below in the comment section below or submit in Whizlabs helpdesk, we will get back to you in no time.
- Top 20 Questions To Prepare For Certified Kubernetes Administrator Exam - August 16, 2024
- 10 AWS Services to Master for the AWS Developer Associate Exam - August 14, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Machine Learning Specialty Certification - August 7, 2024
- Best 15+ AWS Developer Associate hands-on labs in 2024 - July 24, 2024
- Containers vs Virtual Machines: Differences You Should Know - June 24, 2024
- Databricks Launched World’s Most Capable Large Language Model (LLM) - April 26, 2024
- What are the storage options available in Microsoft Azure? - March 14, 2024
- User’s Guide to Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine - March 1, 2024





Hi Neeru,
Thanks for sharing this with everyone. we can understand easily by using this.
Thanks once again.!!
Regards
Hi Sudhakar, thanks for the appreciation!