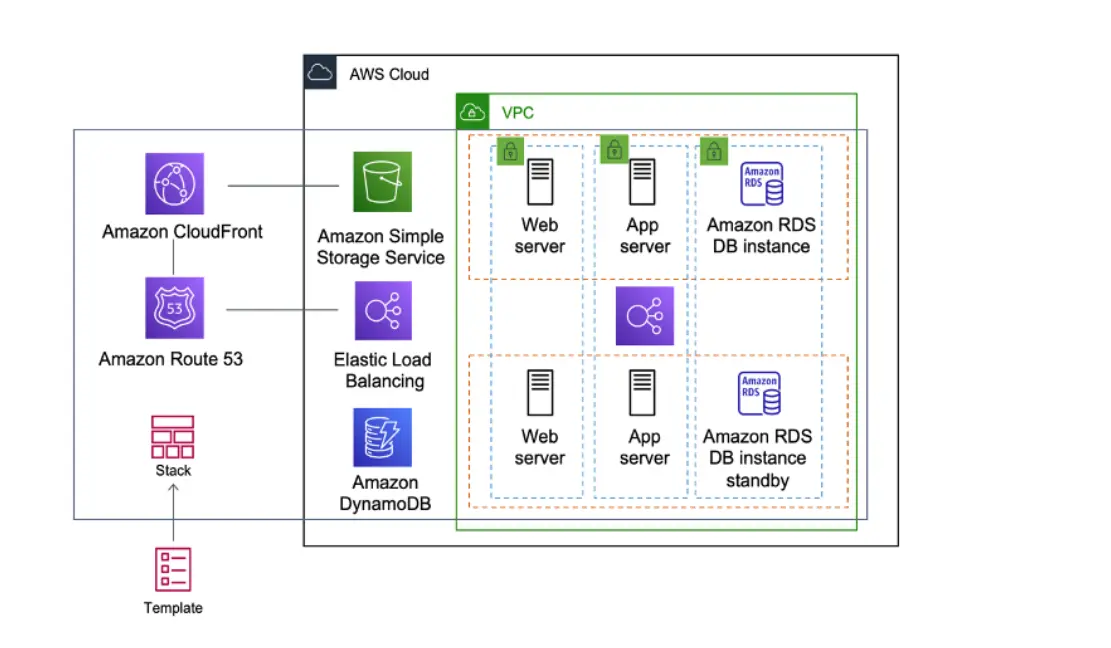
AWS Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02 Certification serves as an excellent entry point for individuals aspiring to enter the field of cloud computing.
To qualify for the position of a Cloud Practitioner, it is essential to acquire a foundational understanding of cloud computing. The key responsibilities of AWS Cloud Practitioner include overseeing a company’s cloud computing strategy.
To ace the interview, enriching your key skills in AWS Cloud and services is essential.
This article provides a collection of AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02 interview questions and answers, curated to assist you in preparation, ensuring you are well-equipped to succeed in your interview and secure a rewarding career in this field.
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Salary
The salary range for an AWS Certified cloud practitioner in India typically spans from ₹2.8 Lakhs to ₹13.2 Lakhs annually. This range is applicable across various experience levels, ranging from less than one year to 7 years.
For reference, the entry-level salary is around ₹2.8 Lakhs, and as the practitioner gains more experience, the salary can increase up to ₹13.2 Lakhs. This underscores the increasing demand for cloud practitioners in India and the recognition of AWS certifications as valuable assets in the IT industry.
In the United States, a skilled AWS cloud specialist could earn a significantly higher annual salary, ranging between $160,000 and $180,000, according to PayScale.
This discrepancy is often influenced by factors such as the cost of living, demand for cloud expertise, and the overall economic landscape in the respective regions. The higher salaries in the U.S. also reflect the premium placed on advanced cloud skills and experience.
Top 20+ AWS Cloud Practitioner Interview Questions
Here are commonly asked AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02 Interview Questions and answers:
1. What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing involves accessing IT resources over the Internet with a pay-as-you-go model. Instead of investing in and managing physical data centers and servers, users can obtain computing power, storage, and databases as required from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
2. What is AWS?
Amazon Web Services is an advanced cloud computing platform released by Amazon. It offers a wide range of services such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
3. What are some of the most common AWS services?
Here are some frequently used AWS services:
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon RDS
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC
- Amazon SNS
- AWS Beanstalk
- AWS Lambda
- AWS Autoscaling
- AWS IAM
4. What is Amazon RDS?
Amazon RDS is a managed relational database service designed for the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases in the cloud. It is utilized for the management of database applications.
5. What is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)?
Amazon Web Services provides EC2, which stands for Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). This cloud computing service from AWS allows you to deploy applications on EC2 servers without concerns about the underlying infrastructure. You have the flexibility to adjust the instance size in response to the application’s incoming traffic.
Also Read: Free Practice Questions on AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Certification
6. Define Elasticity and Scalability in AWS.
“Elasticity” denotes a system’s capacity to automatically adjust resources, expanding or contracting as needed, to sustain consistent performance in response to varying traffic levels, all while minimizing costs. On the other hand, “Scalability” refers to a system’s capability to enhance its capacity for managing increased workloads, achieved either by augmenting resources within the existing setup or by introducing additional configurations.
7. Explain the difference between “scaling up” and “scaling out” in AWS.
| Aspect | Scaling Up (Vertical Scaling) | Scaling Out (Horizontal Scaling) |
| Definition | Increases the capacity of individual resources. | Expands capacity by adding more instances or nodes. |
| Example | Upgrade a single server with more CPU, memory, or storage. | Add more servers behind a load balancer to share the load. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for applications benefiting from increased resources on a single, larger machine. | Ideal for distributed architectures, cloud environments, or applications designed to run on multiple servers simultaneously. |
| Key Benefit | Enhances the capabilities of existing components. | Provides improved scalability, fault tolerance, and performance by distributing the workload. |
| AWS Scenario | Increasing the instance size or upgrading hardware specifications. | Adding more instances to an Auto Scaling Group behind a load balancer. |
| Flexibility | Limited by the maximum capacity of a single resource. | More flexible as you can add instances dynamically to meet increasing demand. |
| Complexity | Generally simpler, involving upgrades or modifications to a single component. | Can be more complex, requiring considerations for load balancing, network configuration, and distributed systems design. |
8. Define AWS IAM.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service designed to enable secure control over access to AWS resources. IAM allows for centralized management of permissions, regulating users’ access to specific AWS resources. It is utilized to govern the authentication (sign-in) and authorization (permissions) of individuals, determining their ability to use various resources.
9. Explain the “Regions” and “Availability Zones” concepts in AWS.
Availability zones are resilient data centers situated within individual AWS regions, each representing a distinct geographic area. Within these zones, there is autonomy in power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. In the event of a complete outage in one availability zone, AWS can seamlessly redirect workloads to another zone in the same region, a feature known as “Multi-AZ” redundancy.
AWS regions function independently of each other, with each region acting as an isolated entity. However, the availability zones within a region are interconnected through low-latency links, facilitating replication and fault tolerance. Opting to host all data and instances in a single availability zone may lead to unavailability if that zone experiences a failure.
This isolation is implemented to manage the workloads with stringent data sovereignty and compliance requirements that mandate user data to stay within a specific geographic region.
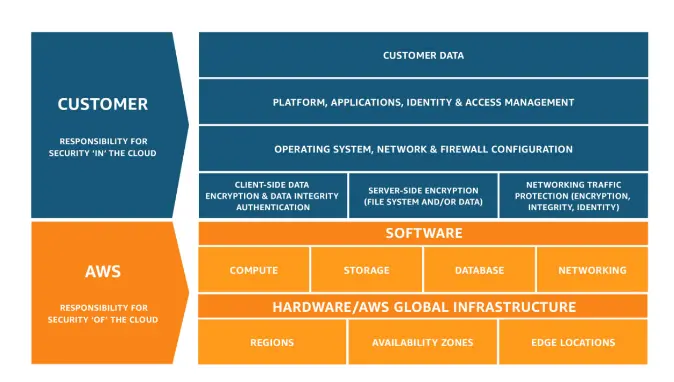
10. What is the Shared Responsibility Model in AWS?
The Shared Responsibility Model is a framework in cloud security that specifies the security responsibilities of both cloud service providers and users to establish accountability. In simple terms, a cloud vendor provides a range of cloud services to its customers, with one party delivering the service, and the other utilizing it. The vendor is responsible for the provision of the service, whereas the user bears responsibility for the consumption of the service.
11. What are the different pricing models available in AWS?
Here are the different pricing models used in the AWS:
| Pricing Model | Description | Pros | Cons | When to Use |
| Free Tier | AWS offers a Free Tier for testing over 100 products, with options like Always Free, 12 Months Free, and Trials. | Ideal for short-term testing, no long-term commitment. | Mostly impractical for long-term production use. | Workload testing, Proof-of-Concepts (PoCs) |
| On-Demand | Default pricing model for AWS EC2, charges per hour or second with no long-term commitment. | No long-term commitment, pay for actual usage hours. | Most expensive option, not suitable for long-running production instances. | Short-term projects, non-production workloads, assessing unpredictable workloads |
| Spot Instances | Allows bidding on unused EC2 capacity at up to a 90% discount, with the risk of termination with short notice. | Up to 90% off On-Demand pricing, suitable for cost-savvy engineers. | Instances can be terminated unexpectedly, complexity in setup. | High fault-tolerant applications, transient workloads like CI/CD pipelines |
| Reserved Instance | Billing discount for On-Demand instances with a commitment to a 1 or 3-year term. | Up to 70% discount, predictable pricing, guaranteed capacity. | Reduced flexibility, requires long-term commitment. | Production applications with predictable, long-term usage |
| Savings Plan | Flexible pricing model offering discounted prices on EC2, Lambda, and Fargate with a commitment to consistent usage. | Up to 72% discount, flexibility (Compute Savings Plans), predictable expenses. | Requires a long-term commitment, excess usage charged at an On-Demand rate. | Predictable, continuous workloads, EC2 nodes, Fargate clusters, or Lambda functions |
12. Define the Principle of Least Privilege and why it is important in AWS.
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) is a foundational concept in information security. It dictates that a user or entity should be granted only the minimum level of access necessary to fulfill a particular task, restricting access to specific data, resources, and applications.
Organizations adhering to the principle of least privilege enhance their security posture by minimizing the potential attack surface and mitigating the risk of malware propagation. This approach ensures that users or entities operate with the minimum permissions essential for their roles, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
13. What is Infrastructure as Code?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is the practice of managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through code, eliminating the need for manual processes and configurations.
In traditional approaches, setting up an application environment involves numerous infrastructure components such as operating systems, database connections, and storage.
With IaC, these components are defined, deployed, and managed using code, allowing for automation, consistency, and version control in the infrastructure deployment process.
14. What is AWS Cloud Adoption Framework?
The AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) utilizes AWS expertise and industry best practices to guide organizations through the process of digital transformation, facilitating the acceleration of business outcomes through innovative use of AWS services. The framework emphasizes the development of specific organizational capabilities crucial for a successful transition to the cloud.
By leveraging AWS CAF, businesses can streamline their cloud adoption journey and harness the full potential of AWS for improved efficiency and innovation.
15. What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing solution that enables you to execute and oversee code without the need to manage servers. With Lambda, you only pay for the actual compute power consumed during the execution of your code. The process is simplified to the submission of your code, and Lambda takes care of the underlying infrastructure and resource management.
16. List different types of cloud services.
Cloud services are typically classified into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Also Read: Top AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Certification CLF-C02 hands-on labs
17. Define VPC.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables you to deploy AWS resources within a logically isolated virtual network that you define. This virtual network closely mirrors a traditional network found in your own data center, while leveraging the scalable infrastructure of AWS. This approach allows you to enjoy the benefits of a familiar network environment while taking advantage of the flexibility and scalability provided by AWS.
18. Define Amazon S3.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is a storage service designed for scalability, with leading capabilities in data availability, security, and performance. It caters to customers of varying sizes and across industries, offering a versatile solution for storing and safeguarding any volume of data.
Amazon S3 serves a wide range of purposes, including data lakes, websites, mobile applications, backup and restore operations, archiving, enterprise applications, IoT devices, and big data analytics. The service also includes management features, allowing users to optimize, organize, and configure access to their data according to specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements.
19. What is EBS in AWS?
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) enables the creation of storage volumes that can be linked to Amazon EC2 instances. After attachment, these volumes can be utilized for various purposes, such as establishing file systems, running databases, or employing them as block storage.
The placement of Amazon EBS volumes occurs in a designated Availability Zone, where automatic replication safeguards against the potential failure of a single component. All EBS volume types come with robust snapshot capabilities and are engineered for superior availability.
20. What is the difference between Redshift and Aurora?
The key differences between Amazon Redshift and Amazon Aurora such as:
| S.No. | Amazon Aurora | Amazon Redshift |
| 1. | Developed by Amazon in 2015. | Developed by Amazon in 2012. |
| 2. | A cloud service by Amazon that is compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL. | A large-scale data warehouse service designed for use with business intelligence tools. |
| 3. | Supports secondary indexes. | Supports restricted secondary indexes. |
| 4. | Compatible with XML format. | Does not support XML format. |
| 5. | Primary database model is Relational DBMS. | Primary database model is Relational DBMS. |
| 6. | Supports Server-side scripting. | Supports user-defined functions for Server-side scripting in Python. |
| 7. | Horizontal partitioning for partitioning. | Supports partitioning methods with Sharding. |
| 8. | Supports SQL query language. | Does not fully support SQL standard. |
| 9. | Supports only one replication method – Master-slave replication. | Also supports various replication methods. |
21. What is auto-scaling, and how does it work?
Auto Scaling, a feature provided by AWS, empowers you to set up the automatic provisioning and deployment of new instances without the need for manual intervention. This functionality ensures that your application can dynamically adapt to varying workloads by automatically adjusting the number of instances to meet demand, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness in your AWS environment.
22. Describe the snowball.
Snowball is a data transport solution at a petabyte scale, utilizing secure appliances to facilitate the seamless transfer of substantial data volumes to and from the AWS cloud. It effectively tackles common issues associated with large-scale data transfers, such as elevated network expenses, extended transfer durations, and security apprehensions.
23. What is Amazon EMR?
Amazon Elastic MapReduce (Amazon EMR) is a web service designed to efficiently process extensive volumes of data quickly and cost-effectively.
Recognized as a leading cloud-based big data platform, Amazon EMR utilizes popular open-source tools such as Apache Spark, Apache Hive, Apache HBase, Apache Flink, Apache Hudi, and Presto. The service simplifies the establishment, operation, and scalability of large-scale data environments by automating tasks like provisioning capacity and optimizing clusters.
24. What is the purpose of creating subnets?
A subnet in your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) represents a specific range of IP addresses. When deploying AWS resources, like Amazon EC2 instances, they are placed within these subnets. Connectivity options include linking a subnet to the internet, other VPCs, and your own data centers. Traffic to and from your subnets is managed by route tables, allowing you to control the flow of data within your network infrastructure.
25. What is AWS Well-Architected Framework?
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is a collection of best practices and strategies aimed at evaluating architectures and implementing designs that can scale effectively over time.
Conclusion
I hope these AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner interview questions for freshers will be invaluable for the upcoming AWS interview preparation. With the continuous growth of the cloud computing field, a solid understanding of AWS core principles becomes progressively valuable.
Thoroughly preparing for these AWS Cloud Practitioner interview questions not only reflects your commitment to the domain but also highlights your knowledge and preparedness to address challenges in the cloud environment.
To further delve into the AWS practically, explore our AWS hands-on labs and AWS sandboxes.
Best of luck, and may your journey in the cloud prove to be both rewarding and successful!
- Top 25 AWS Data Engineer Interview Questions and Answers - May 11, 2024
- What is Azure Synapse Analytics? - April 26, 2024
- AZ-900: Azure Fundamentals Certification Exam Updates - April 26, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Data Engineer Associate Certification - April 19, 2024
- Maximizing Cloud Security with AWS Identity and Access Management - April 18, 2024
- A Deep Dive into Google Cloud Database Options - April 16, 2024
- GCP Cloud Engineer vs GCP Cloud Architect: What’s the Difference? - March 22, 2024
- 7 Ways to Double Your Cloud Solutions Architect Role Salary in 12 Months - March 7, 2024