As DevOps continues to emerge as the predominant practice in IT operations and development, development engineers are actively involved throughout the entire software development lifecycle, encompassing design, development, and production support.
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins helps to understand their distinct roles and functionalities in the realm of DevOps automation.
In this blog, we list out the distinctions among Kubernetes, Docker, and Jenkins models, outlining their respective advantages and drawbacks. Let’s dive in!
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins: Definition
Here are the key definitions of Kubernetes, Docker, and Jenkins:
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source container management system created by Google and it helps to handle the containerized program in varied categories of physical, virtual, or cloud environments.
This flexible tool handles intricate applications that run on millions of independent servers. Individuals who have legit credentials can be able to manage containerized software such as Kubernetes.
At a higher level, Kubernetes adheres to a client-server architecture, comprising key components:
- Master Node: Responsible for upholding cluster integrity, the master node monitors component interactions and aligns the actual system state with the desired state.
- Etcd: Functioning as a distributed key-value storage system, Etcd maintains cluster state records, including information on the number of pods, deployment states, namespaces, and service discovery details.
- Worker Nodes: Managed by the master node, worker nodes execute containers. Each component (excluding Etcd) further consists of distinct parts, each serving a specific purpose. Understanding these parts provides insight into their respective functions.
Features of Kubernetes
The distinct features of Kubernetes such as:
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing: In Kubernetes, containers are assigned unique IP addresses and DNS names, which DevOps engineers can use for load balancing purposes.
- Resource Planning and Placement: Deciding where to deploy containers within the cluster is a critical task, taking into account the required resources and expected duration of operation.
- Auto Scaling: Kubernetes can automatically adjust the number of containers based on CPU utilization, and vertical scaling can be triggered using command-line tools (CLI).
- Self-Repair: Kubernetes possesses a unique feature that can automatically restart malfunctioning containers. If nodes become unresponsive, containers are redeployed on other nodes.
- Storage Management: Kubernetes enables the orchestration of storage, allowing clients to scale network storage systems and keep data localized.
- Batch Processing: Kubernetes efficiently manages both batch jobs and continuous integration workloads, including the restoration of containers that encounter issues.
- Configuration Management and Secrets: The system securely stores sensitive information in a module called “Secrets,” which can be used to configure software without the need to rebuild the image.
Docker
Docker is also an open-source tool for achieving automation in application classification in terms of lightweight and transferable containers. It uses Linux-based kernel attributes and employs a sandbox environment for the virtual environment configuration.
Even though container virtualization seems old-fashioned, top firms such as Red Hat and Microsoft rely upon Docker for the DevOps.
Features of Docker
- Easy Configuration: Docker simplifies system configuration across various environments, making it a convenient choice.
- Enhanced Productivity: Docker streamlines technical configuration and accelerates application deployment in remote environments, boosting productivity.
- Application Isolation: Docker employs containers to create isolated environments for running applications, ensuring that each application runs independently from others.
- Docker Swarm: Docker Swarm is a tool for clustering and scheduling Docker containers, using an API as its interface. It efficiently manages a group of Docker hosts as a single virtual host.
- Routing Mesh: This feature directs incoming requests for published ports on available nodes to active containers, ensuring connectivity between nodes and containers even when no specific task is running on the node.
- Services: Services in Docker allow you to monitor the state of containers within each cluster. Each service represents a container awaiting deployment, and Docker Swarm efficiently schedules them across nodes in a queue.
- Security Management: Docker’s security management feature securely stores critical information within the Swarm and enables controlled access to secrets.
Jenkins
Jenkins is a free automation tool known for its numerous plugins designed for Continuous Integration. It’s primarily used for developing and testing software projects and applications, making it easier for IT teams to integrate project changes seamlessly.
With Jenkins, you can streamline the software development cycle through comprehensive automation.
Key Features of Jenkins
- Simple Installation: Jenkins is a platform-agnostic, Java-based program that can be effortlessly deployed on Windows OS, Mac OS, and Unix systems.
- User-Friendly Configuration: Its web-based interface provides an intuitive configuration system, complete with error checking and a helpful “Ask for Help” feature.
- Abundant Plugins: Jenkins seamlessly integrates with a wide range of CI/CD toolchain tools, thanks to its extensive collection of plugins.
- Extensibility: Jenkins is highly adaptable and extensible, thanks to its plugin architecture, which opens up a world of possibilities for customization.
- Efficient Task Distribution: Jenkins can distribute tasks across multiple machines, leading to faster and more efficient task delivery.
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins Differences
| Feature | Kubernetes | Docker | Jenkins |
| Primary Purpose | Automates deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications | Facilitates application development, packaging, and running within containers | Automates the software delivery process, including building, testing, and deploying applications |
| Scalability | Suitable for large-scale deployments | Ideal for smaller deployments | Scalable through plugins and extensions |
| Complexity | High complexity | Lower complexity compared to Kubernetes | Moderate complexity |
| Networking | Offers advanced networking capabilities | Provides basic networking capabilities | Networking capabilities depend on plugins and extensions |
| Load Balancing | Includes built-in load balancing support | Relies on external tools for load balancing | Load balancing capabilities depend on plugins and extensions |
| Persistent Storage | Offers built-in support for persistent storage | Requires external tools for persistent storage | Persistent storage capabilities depend on plugins and extensions |
| Monitoring and Logging | Provides advanced monitoring and logging capabilities | Offers basic monitoring and logging features | Monitoring and logging capabilities depend on plugins and extensions |
| CI/CD Integration | Integrates with CI/CD tools | Integrates with CI/CD tools | Offers built-in CI/CD capabilities |
| Community Support | Benefits from a large and active community | Benefits from a large and active community | Benefits from a large and active community |
| Licensing | Open-source and freely available | Open-source and freely available | Open-source and freely available |
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins: Pros and Cons
Kubernetes Advantages
- Scalability for dynamic resource allocation.
- Automated deployment, scaling, and updates.
- High availability with redundancy and failover.
- Flexibility for diverse application types.
- Strong community support.
Kubernetes Disadvantages
- Steeper learning curve
- Resource-intensive
- Limited customization options
Docker Advantages
- User-friendly container management
- Portability across supporting systems
- Lightweight and quick deployment
- Versatile for different applications
Docker Disadvantages
- Security is not as robust as traditional VMs
- Lack of automatic scaling
- Complex networking in larger setups
Jenkins Advantages
- Automation of development processes
- Seamless integration with Docker and Kubernetes
- High configurability and extensibility
- Abundant plugins for added functionality.
- Open source and cost-effective.
Jenkins Disadvantages
- Initial complexity in setup.
- Ongoing maintenance and updates.
- Security risks without proper measures.
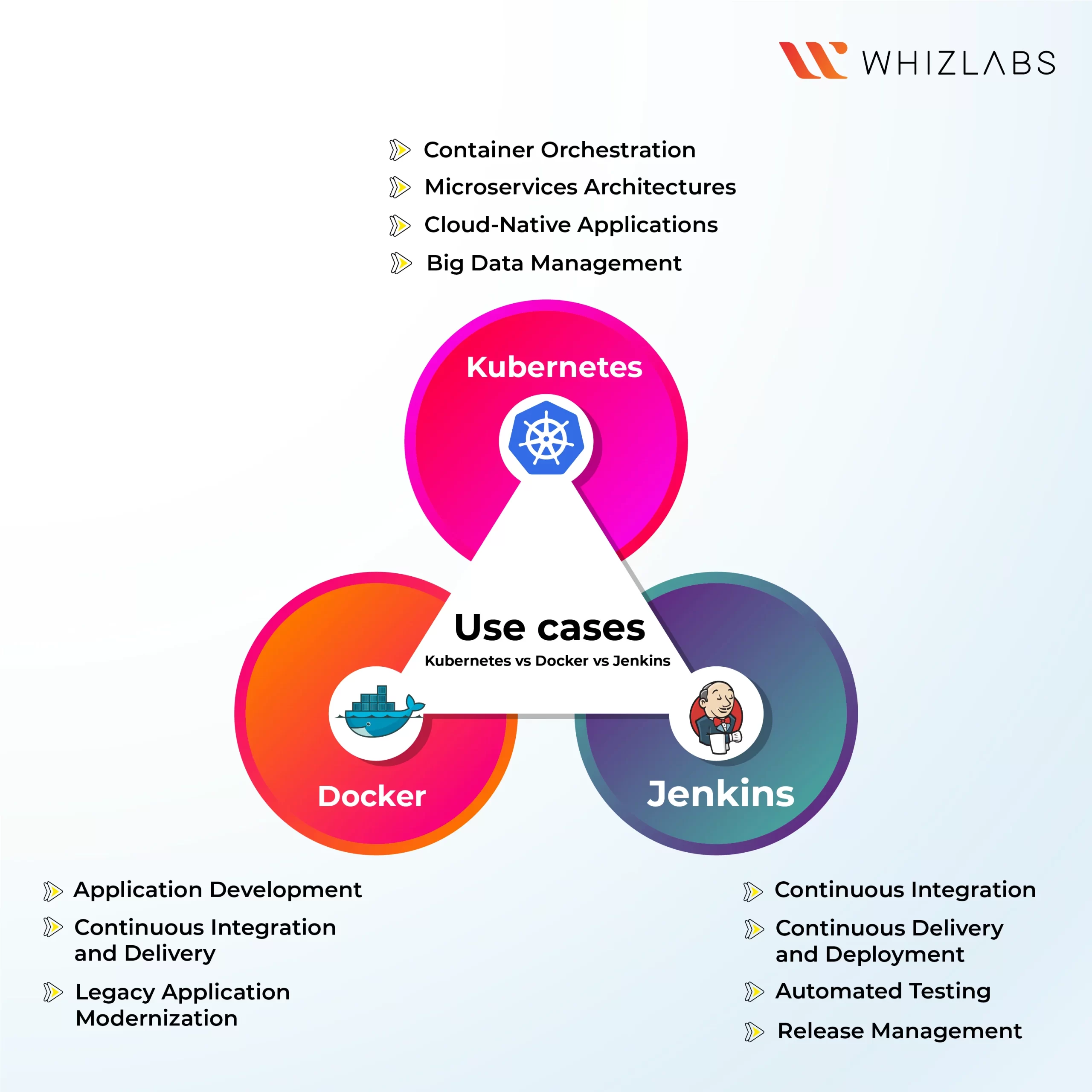
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins: Use Cases
Kubernetes Use Cases
- Container Orchestration: Kubernetes excels in the realm of container orchestration, where it efficiently manages and deploys containers at scale.
- Microservices Architectures: Kubernetes is particularly well-suited for microservices, enabling the independent deployment and management of smaller application components.
- Cloud-Native Applications: Kubernetes is widely adopted for deploying cloud-native applications, tailored to run in cloud environments, leveraging the benefits of cloud computing.
- Big Data Management: Kubernetes finds applications in managing big data applications, especially those requiring real-time processing and analysis of substantial data volumes.
Docker Use Cases
- Application Development: Docker is a popular choice for application development, simplifying the creation, testing, and deployment of applications within containers.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery: Docker is a valuable asset in continuous integration and delivery pipelines, streamlining the building and deployment of applications for faster and more efficient workflows.
- Legacy Application Modernization: Docker aids in modernizing legacy applications by containerizing them, facilitating their management and deployment in a more flexible and scalable manner.
Jenkins Use Cases
- Continuous Integration: Jenkins is widely employed for continuous integration, automating the build and testing processes whenever code changes are made.
- Continuous Delivery and Deployment: Jenkins is crucial for continuous delivery and deployment, automating the deployment of code to production environments once it has successfully passed all tests.
- Automated Testing: Jenkins is a valuable tool for automated testing, simplifying the process of code testing and enabling early bug detection in the development cycle.
- Release Management: Jenkins serves as an effective platform for release management, streamlining the tracking and management of software releases and changes to the codebase.
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins: Career Opportunities
Kubernetes, Docker, and Jenkins are all popular technologies in the realm of DevOps and containerization, and each plays a distinct role in the software development and deployment lifecycle. Here’s a brief overview of each along with brief insights into potential career opportunities.
You can try for the various roles if you are familiar with technologies such as Kubernetes, Docker, and Jenkins:
| Technology | Job Titles |
| Kubernetes |
|
| Docker |
|
| Jenkins |
|
Now let’s see the salary range for the above roles:
Kubernetes Administrator salary in India ranges between ₹ 1.2 Lakhs to ₹ 27.4 Lakhs with an average annual salary of ₹ 8.7 Lakhs.
Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins Which is Better?
The choice between Kubernetes and Docker hinges on your unique needs. Several factors should guide your decision:
- Complexity: Kubernetes offers advanced features like orchestration, scaling, and multi-container management, making it more complex but suitable for large-scale deployments. Docker is simpler but may lack these capabilities.
- Scalability: Kubernetes excels in scaling containers and applications seamlessly. Docker is also scalable, but it might require additional tools for the same level of scalability.
- Integrations: Kubernetes integrates well with various tools like CI/CD pipelines, monitoring, and cloud providers. Docker has integrations too, but they may not be as comprehensive as Kubernetes.
- Cost: Kubernetes typically demands more resources and infrastructure, which can increase deployment and management costs. However, its added features may justify the cost.
If you require a robust and flexible solution for large-scale deployments, Kubernetes is the preferred choice. For simpler, smaller deployments, Docker may suffice. Ultimately, your choice should align with your specific needs, so it’s crucial to carefully assess both options before making a decision.
FAQs
Can we use Kubernetes without Docker?
You can use Kubernetes without Docker. While Docker is a popular platform for containerization, it’s not the exclusive option. As long as you have a container runtime, Kubernetes can effectively manage containers. While Docker is a common choice, it’s important to note that it’s not a mandatory requirement for Kubernetes to function.
Is Kubernetes difficult to learn?
Learning Kubernetes has historically been considered challenging due to its steep learning curve. However, over the years, Kubernetes has undergone improvements, making it more accessible. The core Kubernetes project has become easier to install and maintain. Additionally, major cloud platforms now offer managed services that simplify the usage of Kubernetes, reducing the overall effort required.
How long does it take to learn Docker and Kubernetes?
The time it takes to learn Docker and Kubernetes can vary based on several factors, including your prior experience, the depth of knowledge you aim to acquire, and the resources you use for learning. However, if you dedicate focused time and consistent practice, it’s feasible to grasp the fundamentals of Docker within 30 days.
Is Kubernetes still in demand?
Individuals with experience and expertise in Kubernetes are in high demand in the job market. Such professionals are likely to attract lucrative opportunities and substantial compensation through various projects.
Conclusion
Hope this blog explains the key differences between Kubernetes vs Docker vs Jenkins. The synergy between Kubernetes, Docker, and Jenkins empowers DevOps teams to build, test, and deploy applications with agility and efficiency, contributing to the seamless integration of development and operations in the software development lifecycle.
To truly immerse yourself in a hands-on learning experience in DevOps, dive into our interactive hands-on labs and sandboxes.
- Study Guide DP-600 : Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric Certification Exam - June 14, 2024
- Top 15 Azure Data Factory Interview Questions & Answers - June 5, 2024
- Top Data Science Interview Questions and Answers (2024) - May 30, 2024
- What is a Kubernetes Cluster? - May 22, 2024
- Skyrocket Your IT Career with These Top Cloud Certifications - March 29, 2024
- What are the Roles and Responsibilities of an AWS Sysops Administrator? - March 28, 2024
- How to Create Azure Network Security Groups? - March 15, 2024
- What is the difference between Cloud Dataproc and Cloud Dataflow? - March 13, 2024