In the digital era, cybersecurity plays a major role in everyone’s lives. From safeguarding personal data to securing company data, knowing the cybersecurity terms is essential for anyone who wants to enter into the cybersecurity field.
In this article, we will explore the important cybersecurity terms that you need to know. Some of the key terms covered such as common cybersecurity terminologies, Cyber Threat Actors and Methods, Emerging trends, and cybersecurity certifications. To gain a solid understanding of cybersecurity terminology, consider pursuing foundational cybersecurity certifications such as the SC-100 certification.
Let’s dive in!
Common Cybersecurity Terms
Here are some common Cybersecurity terms you must know when you are in the cybersecurity field.
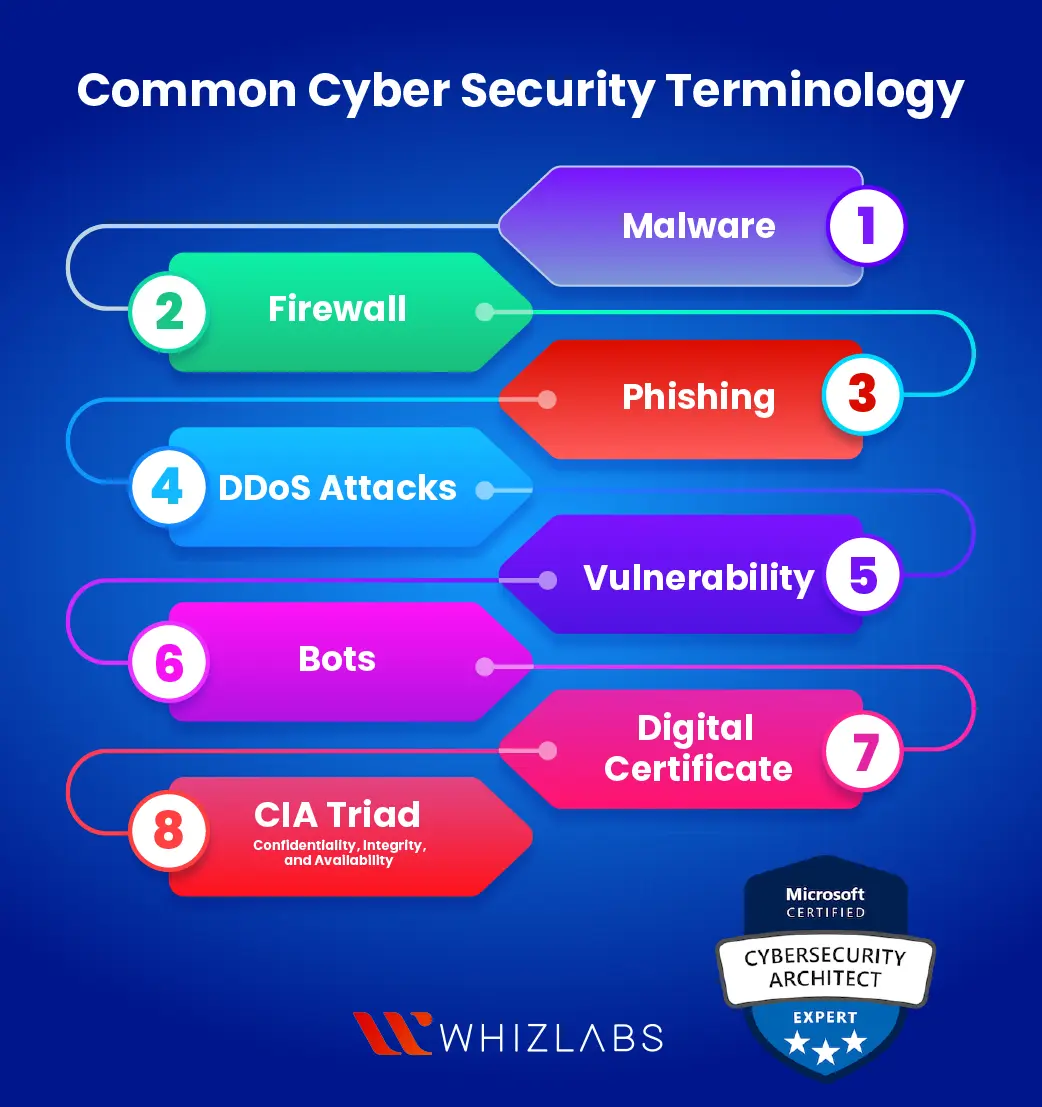
Malware
The term malware stands for malicious software and it contains harmful software programs to harm or gain unauthorized access into the computer systems. Some of the common malware include worms, trojans, viruses, and ransomware.
Firewall
It refers to network security devices that help to monitor and control the network traffic. It acts as a defender between the trusted and untrusted external network, which allows the data packets to be blocked based on predefined security rules.
Phishing
This kind of cyberattack method is used by the attackers and employs deceptive messages, emails, or websites to make the individuals reveal sensitive data such as financial data or login credentials.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks make the target system or network to be flooded with traffic and thus the user cannot to be able to access those services. To execute this kind of attack, the attackers use the compromised network such as botnets.
Vulnerability
Vulnerability refers to weaknesses in the system, application, and data that are exploited mainly by hackers with the intention of compromising network security. To nullify this kind of attack, we have to identify and patch the vulnerabilities that exist in the network.
Bots
A bot represents an application or script specifically created for executing repetitive and automated functions. While certain bots serve legitimate functions, such as chatbots designed to respond to frequently asked questions on websites, others are employed for malicious intent. These bots engage in activities like distributing spam emails or orchestrating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
With the increased usage of bots, distinguishing between benign and harmful ones, or even bots from human users becomes increasingly challenging. This growing complexity underscores the escalating threat that bots pose to both individuals and organizations.
Digital Certificate
A digital certificate, also referred to as an identity certificate or public key certificate, serves as a secure key for facilitating data exchanges over the Internet. Think of it as a digital file securely embedded in a device or hardware component. Its primary function is to authenticate the device or server during the transmission of data. In essence, this certificate ensures that data sent and received between two devices or a device and a server remains confidential and secure.
Also Read : A Quick Introduction to Cybersecurity
CIA Triad – Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
The CIA triad offers a valuable framework for both establishing and assessing an organization’s cybersecurity systems and policies.
Cyber Threat Actors and Methods
Hackers
Hackers refer to individuals or groups who have the advanced technical skills to gain unauthorized access to systems, networks, or data for financial gain.
Cybercriminals
The cybercriminal refers to an individual who commits a cybercrime, where they use the computer as the primary target or tool as both.
Insiders
Insiders in an organization are individuals who either intentionally or unintentionally misuse their access privileges, posing a significant challenge when it comes to detecting and preventing security breaches.
Social Engineering
This refers to a specific kind of attack that manipulates human behavior to access sensitive information or infiltrate secure systems.
Password Cracking
Password cracking involves the process of attempting to guess or forcibly break a password in order to gain unauthorized access to a system or account.
Ransomware
This is a form of malicious software (malware) that locks a victim’s files or data behind encryption and then demands a ransom payment in exchange for providing the decryption key.
Protective Measures
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software helps to detect, defend, and destroy malware from computers and networks. The software will be involved in scanning malicious code and patterns to retain the system in secured mode.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication MFA brings an additional layer of security by holding the user’s multiple identities and it requires multiple forms of identification for granting access. Some of the Multi-factor authentication identities such as passwords, tokens, and biometrics.
Patch Management
Patch management involves the process of updating the systems and software in a regular manner to identify vulnerabilities. If the patching process is not carried out in a periodic manner, the system will be exposed to harmful attacks and cyber threats.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation partitions the network into smaller and isolated segments to restrict breaches and harden the network security to defend against the attacks exploited by intruders.
Incident Response Plan
The incident response plan includes the aligned procedures for detecting, managing, and defending security incidents. To minimize the damage that occurs during the cyberattack, a well-defined incident response plan is required.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN is a secure connection established between devices over the internet. It effectively shields all data transmitted between these devices by encrypting it, ensuring confidentiality and security.
Types of Cybersecurity
Application Security (AppSec)
Application security, often referred to as AppSec, involves the practice of integrating and testing security measures within web applications. Its purpose is to shield these applications from potential threats. Vulnerabilities, security misconfigurations, and design flaws can be exploited, leading to issues such as malicious code injections, exposure of sensitive data, system compromise, and other harmful consequences.
Notably, AppSec holds significant importance as the application layer is particularly susceptible to breaches.
Cloud Security
Cloud security is a relatively recent addition to the cybersecurity landscape. It revolves around safeguarding cloud computing environments, applications, and data stored in the cloud. While cloud providers implement their own security measures, clients also have a shared responsibility for configuring and using their cloud services securely.
Critical Infrastructure Security
Critical infrastructure security safeguards the essential infrastructure elements of a region or nation. This encompasses both physical and digital security, systems, and assets that contribute to physical security, economic stability, public health, and safety.
Examples include the electricity grid, hospitals, traffic management systems, and water supply networks. Given the digital nature of critical infrastructure, it is vulnerable to cyberattacks and requires robust protection.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security
IoT security focuses on securing an expansive array of internet-connected devices that can communicate independently. This category includes devices like baby monitors, printers, security cameras, and motion sensors.
Many of these devices collect and store personal information, making them attractive targets for malicious actors seeking to steal identities. Therefore, robust security measures are necessary to protect against unauthorized access and other potential threats.
Network Security
Network security is the practice of defending computer networks and data against threats, both external and internal. This involves implementing identity and access controls, such as firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and two-factor authentication (2FA). Network security typically comprises three main categories: physical, technical, and administrative, all of which aim to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to network components, data, and the network infrastructure itself.
Each of these cybersecurity domains plays a crucial role in safeguarding digital assets and ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and systems.
Emerging Trends
AI and Machine Learning in Cyber Security
Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning technologies are widely employed in the cybersecurity field to defend against various threats. It is possible by automated threat detection, enhancing anomaly detection, and streamlining the incident response.
IoT Security
In today’s interconnected world, various security challenges evolve. This opens the way to the development of IoT devices. However, ensuring the security of the IoT systems is a major concern.
Cloud Security
With the increased demand for cloud computing, achieving data retained in the cloud is of paramount importance. The adoption of cloud security solutions helps in addressing this kind of challenge.
Know More : Top Cybersecurity Experts & Influencers to follow in 2024
Cybersecurity Compliance
GDPR
The compliance standard such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) refers to European Union regulations, which mainly deal with data privacy and protection. To handle the EU data of the users, compliance is mandatory.
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) employs data protection standards to protect the sensitive health data of a patient in the healthcare industry.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 refers to the international standard used for information security management systems. Many organizations use it as a framework for establishing and maintaining robust security practices.
Cyber Security Certifications
In the cybersecurity world, various cybersecurity threats and risks may evolve, and certifications play a major role in showing your expertise, and skills and improving your professional credibility. Here, we have explored three major cybersecurity certifications that are more valuable in the industry:
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification is considered one of the most recognized certifications in the cybersecurity industry. It is released by a globally recognized nonprofit organization (ISC)² for ensuring information security.
CISSP certification is designed mainly for professionals who have an in-depth understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices.
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification released by the International Council of E-Commerce Consultants is designed mainly for professionals who want to enhance their skills in understanding the tactics and techniques of hackers. By holding this certification, you can be able to identify and address the vulnerabilities in the systems and networks.
To clear up this certification, you must have ethical hacking skills for securing the systems by finding the system’s weaknesses before the attackers exploit them. The key topics covered in this certification involve ethical hacking concepts, scanning, enumeration, hacking, malware threats, sniffing, social engineering, and so on.
CEH certification offers the right tools and knowledge for assessing the security of an organization in a proactive manner.
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
The Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification is issued by a global association ISACA for governing information, risk management, and cybersecurity. CISM is designed for professionals who have engaged in managing and governing information security programs. CISM Certification can be suitable for the following job roles such as IT governance, IT risk management, and security management.
FAQs
What are the 5 C’s of cybersecurity Terms?
Whether you’re a small business or a big one, understanding the 5 Cs of cybersecurity is really important. These are Change, Compliance, Cost, Continuity, and Coverage. They give you a solid plan to protect your digital stuff.
What are the core terms used in cyber security?
In the “CIA triad,” the trio of letters represents Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. This widely recognized model serves as the cornerstone for designing security systems. It aids in identifying weaknesses and devising strategies to address them.
What are the 3 A’s of cybersecurity terms?
AAA stands for Authentication (confirming identity), Authorization (granting permission), and Accounting (keeping a record).
What are the common cybersecurity terms used?
Some of the common cybersecurity terms are malware, phishing, threat, encryption, attacker, CIA Triad, and so on.
Conclusion
Hope this article covers the essential cybersecurity terms required in our modern digital era. It doesn’t matter if you’re an IT expert, a business owner, or simply someone who uses the internet occasionally must know these terms to shield yourself and your valuable assets from online dangers.
We’ve explored fundamental concepts like malware, firewalls, encryption, and phishing. We’ve delved into the motivations and techniques of cyber attackers and talked about how to stay safe with tools like antivirus software, multi-factor authentication, and plans for handling incidents. We’ve also mentioned new developments like AI and IoT security, along with compliance rules such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
By familiarizing yourself with these cybersecurity terms and staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends, you can be confident in your ability to tackle the continually changing cybersecurity arena. If you want to level your practical knowledge in cybersecurity, try our hands-on labs and sandboxes.
- 7 Pro Tips for Managing and Reducing Datadog Costs - June 24, 2024
- Become an NVIDIA Certified Associate in Generative AI and LLMs - June 12, 2024
- What is Azure Data Factory? - June 5, 2024
- An Introduction to Databricks Apache Spark - May 24, 2024
- What is Microsoft Fabric? - May 16, 2024
- Which Kubernetes Certification is Right for You? - April 10, 2024
- Top 5 Topics to Prepare for the CKA Certification Exam - April 8, 2024
- 7 Databricks Certifications: Which One Should I Choose? - April 8, 2024