Preparing for a business to be run in a successful manner needs a transition from on-premises hardware to the cloud to fulfill the computing needs. With time, technology, and various other technology-related factors, everything becomes digitalized, specifically, it is possible with technology like “cloud computing”. Becoming digitized can make your move to a fast-paced world.
Even though cloud technology furnishes numerous benefits, it still faces various security risks and threats. This kind of issue makes some people stand back while coming to cloud computing adoption.
To make a pull stop for such a concern, Microsoft Defender emerged as an effective solution to level up security for cloud computing. This blog takes you on how to enable cloud security with the usage of Microsoft Defender.
Let’s dig in!
Reasons to Adopt Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is an Azure-based security platform that helps with threat detection and security posture management for managing the hybrid cloud workloads.
Azure offers a highly scalable, feature-enabled platform for the implementation of dynamic applications, which have inherent security challenges. Let’s have a glance at common issues faced in cloud computing:
Rapidly Changing Workloads
One of the pros of hosting the applications on Azure is that infrastructure can be scaled to handle altering workloads. However, as instances get replicated, web security infrastructure need not to scale accordingly.
It can become true with hybrid cloud architectures, as the traditional security platforms lack the flexibility to implement security controls in a consistent way when the cloud workloads tend to scale up and down.
High Level of Expertise
The main hindrance to the implementation of cloud technology such as lack of expertise and knowledge to ensure security for the distributed networks. As per the survey, 76% of the organizations adopt multiple clouds, which brings complexities and expertise knowledge also required.
Vulnerability Detection and Threat Management
If you want to carry out threat detection and threat management in an easier way, then you must opt for Microsoft Defender for the cloud. Apart from this, it also aids in offering security recommendations and hardening security for the services and resources.
As Microsoft Defender is built on the basis of threat intelligence services, it helps to offer wide range of data based protection solutions for balancing workloads. Moreover, it also furnishes some of the services, which includes, prevention of the security threats, generation of the security alerts to the security teams about the upcoming issues and holistic view of the entire infrastructure.
How to Set Up Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Here are some steps to configure and run Azure Security Center for hybrid based workloads.
Step 1: Enabling Azure Security Center
To set up Microsoft Defender for Cloud service, you have to sign in to the Azure portal. After signing in, you can access various services and features of Microsoft Azure via web UI.
Now, select the Microsoft Defender for cloud by simply searching in the search bar. Now click on the upgrade option in the dashboard to enable the Microsoft Defender for cloud and it automatically enables Azure defender.
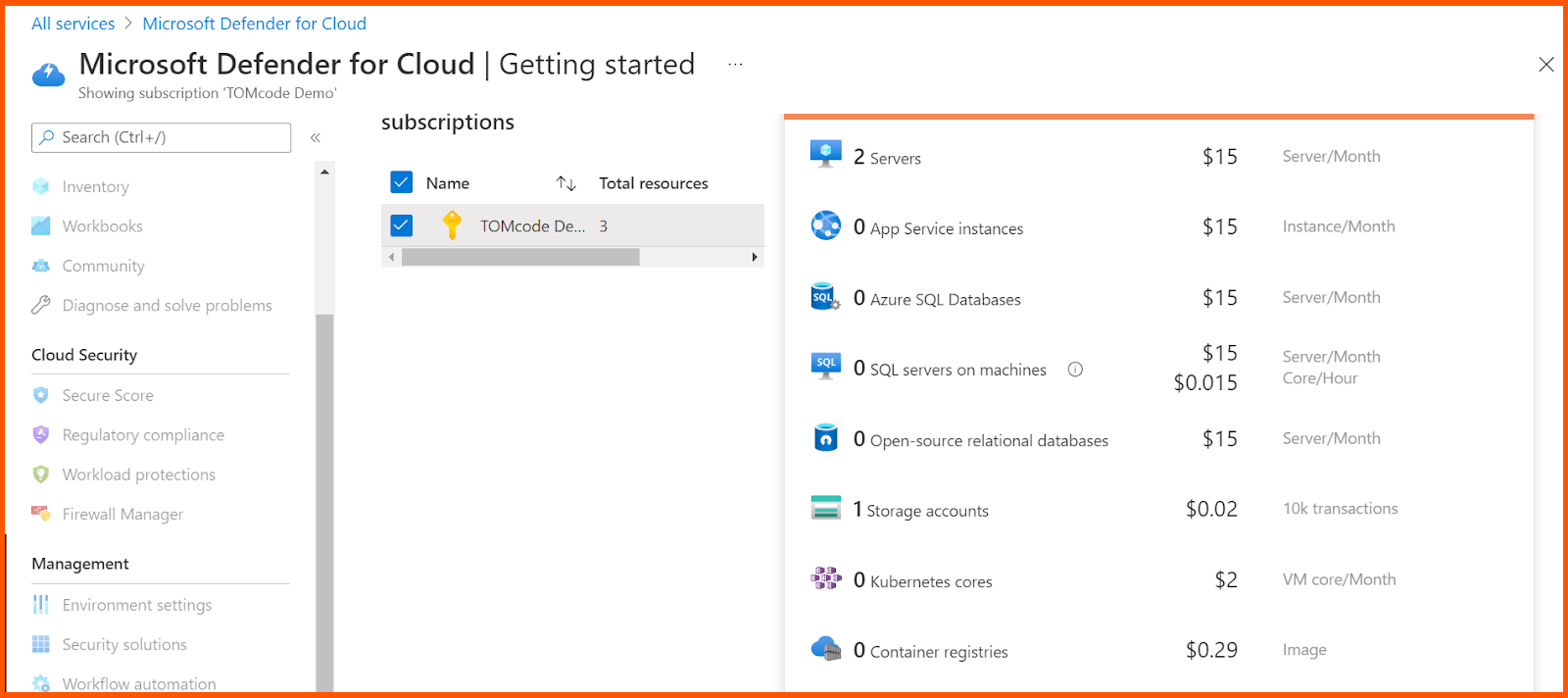
Overview is a visual dashboard that you may use to see the many components of your level of security. It shows coverage details, security alerts, and much more. You can click on any element to learn more about it. You may find out about and evaluate the security of your workloads using this dashboard, as well as detect and reduce risks.
You may examine, modify, and add subscriptions that have Defender for Cloud activated by going to the Subscriptions option in the Overview dashboard.
Once it is set up, MDC provides security suggestions on how to enhance the security level of connected resources,and how to harden the security posture of cloud based workload. The dashboard also helps in assessment of inventory of the resources, showing off security posture for easier data management.
All monitoring components will immediately deploy and start running as soon as Defender for Cloud is enabled. Turn the plan off if you want to deactivate any of the plans. The components of the plan won’t collect any data, but the extensions they use won’t be removed either.
Step 2: Configuring Auto-Provisioning
The main reason for doing configuration on Auto provisioning is to eliminate overhead by just installing the required agents, to ensure rapid security coverage for the hybrid based cloud resources.
Auto provisioning gets disabled by default, and thus Azure makes it easier for the collection of data while monitoring.
To achieve this, Just click on the environment settings on Microsoft Defender as illustrated below:
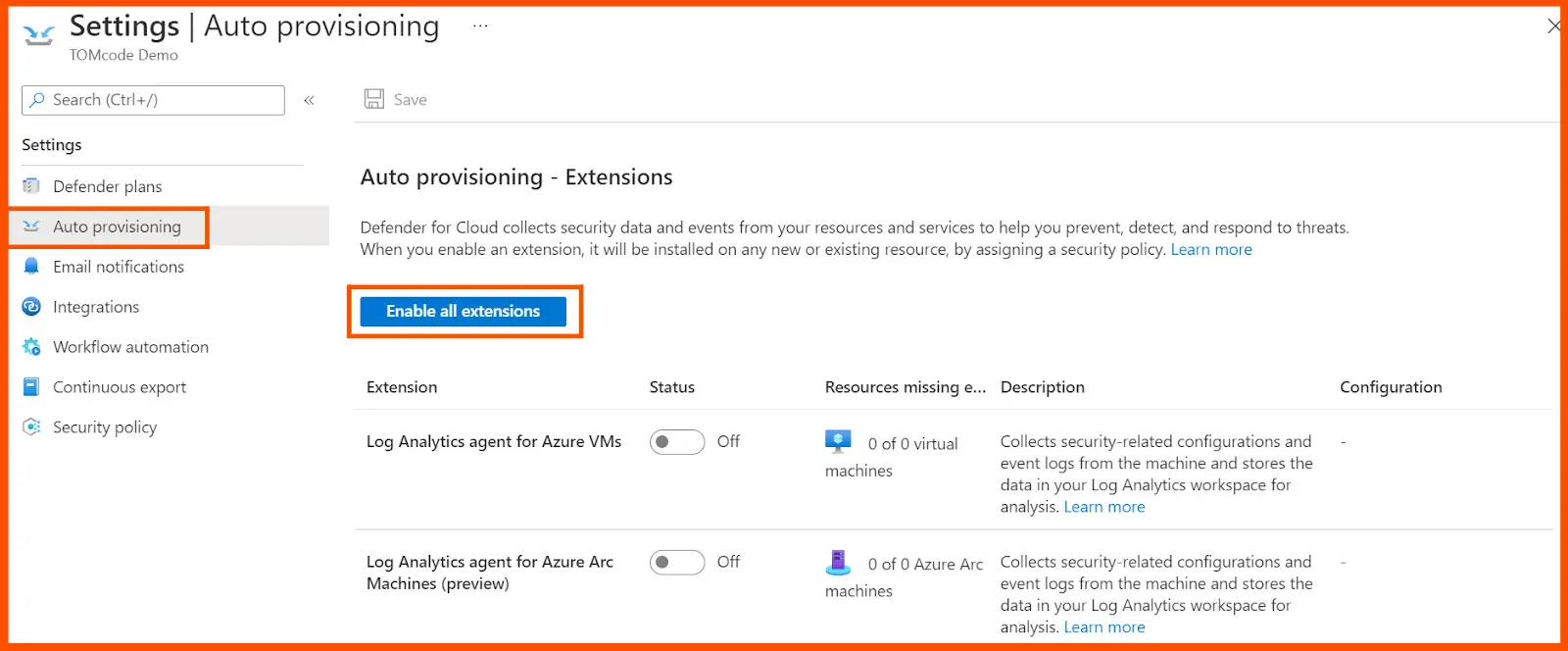
Choose the relevant subscription and then move on to the auto-provisioning page, and click on enable all extensions.
Defender for Cloud continuously evaluates all of your cloud resources to produce a score. Each cloud would be rated differently if Google Cloud and AWS were integrated. The score also includes cautions and suggestions, which, when clicked, guide users through fixing the problems.
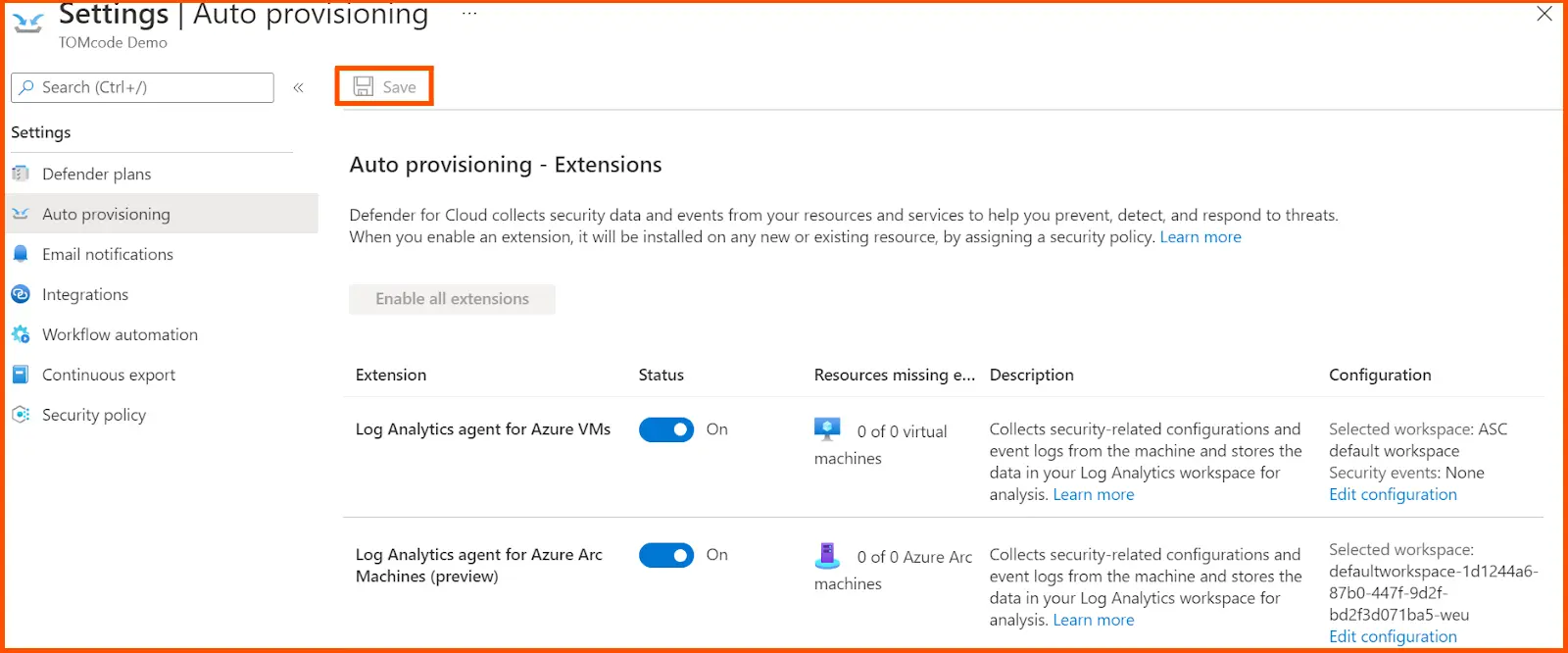
After doing this, the Extensions menu get pop-up. Click on Apply to ON all the default auto-provisioning settings for configuring the workspace, selection of workspace, and vulnerability assessment. Now save all the activities to activate the subscription plan.
This kind of activity automatically installs the required extensions to collect the data to gain visibility into security status for the various computing resources, such as IaaS containers, Virtual Machines, and scale sets, and non-Azure machines.
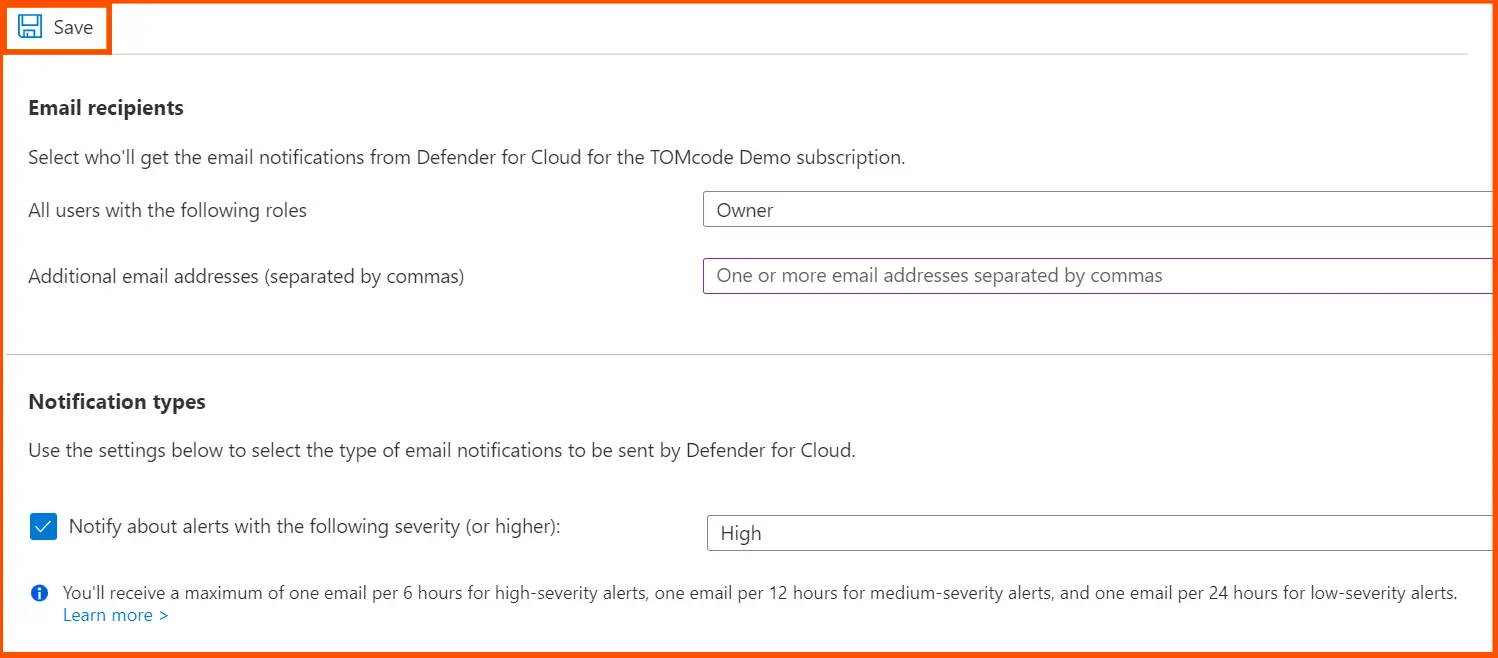
In the Auto provisioning menu, click on Email notifications.
Now, click on the roles that are desired for the recipients, and key in specific email addresses in the email addresses field, which are separated by a comma.
Now choose the severity level of the notifications that are sent to the selected users, and then click on Save to verify the selection.
Step 4: Connecting with Azure VMs
Once auto-provisioning is enabled, the renamed version of Microsoft Defender for Cloud immediately establishes a connection with Azure VMs. You can use Azure Arc to link with Microsoft Defender plans for non-Azure machines. Workloads in AWS or GCP can be monitored and secured with Defender for Cloud. Microsoft has useful documentation that explains how to quickly link your AWS or GCP accounts as independent environments.
Step 5: Creating Auto-Response for Alerts
Using Azure Resource Management (ARM) templates, operations teams can configure automated responses to specific security alarms. The infrastructure and configuration of your project can be defined using these templates, which are JSON files. This will allow you to build workflow automation that launches a logic app when Defender receives particular security alerts.
Step 6: Using the Overview Dashboard
Microsoft Defender has the ability to scan resource configurations and evaluate them against regulatory standards and frameworks in addition to providing a summary of linked resources and their security posture.
From the platform’s menu, select Regulatory compliance to add a standard to the dashboard.
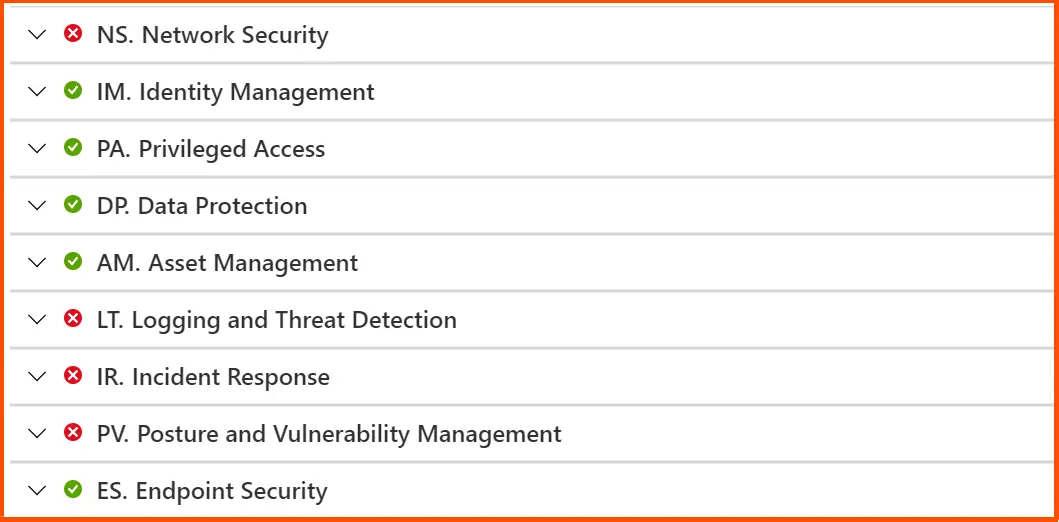
Teams can strengthen their security posture by viewing the compliance status of key security factors in a hybrid environment on the following page. By choosing a certain benchmark and reviewing various sets of assessments, this can be honed in on the fundamental problem.
Your subscriptions can use built-in or custom security policy definitions. Defender for Cloud will look after them and make suggestions in light of them.
Any of these policies can be assigned via the Azure interface, PowerShell, or the Azure CLI. From Azure Policy, policies can be enabled or disabled, and they can be grouped according to targets as part of a larger security campaign. Meeting regulatory compliance norms is one situation where this functionality comes in handy. Visit Microsoft Learn for additional information about this problem.
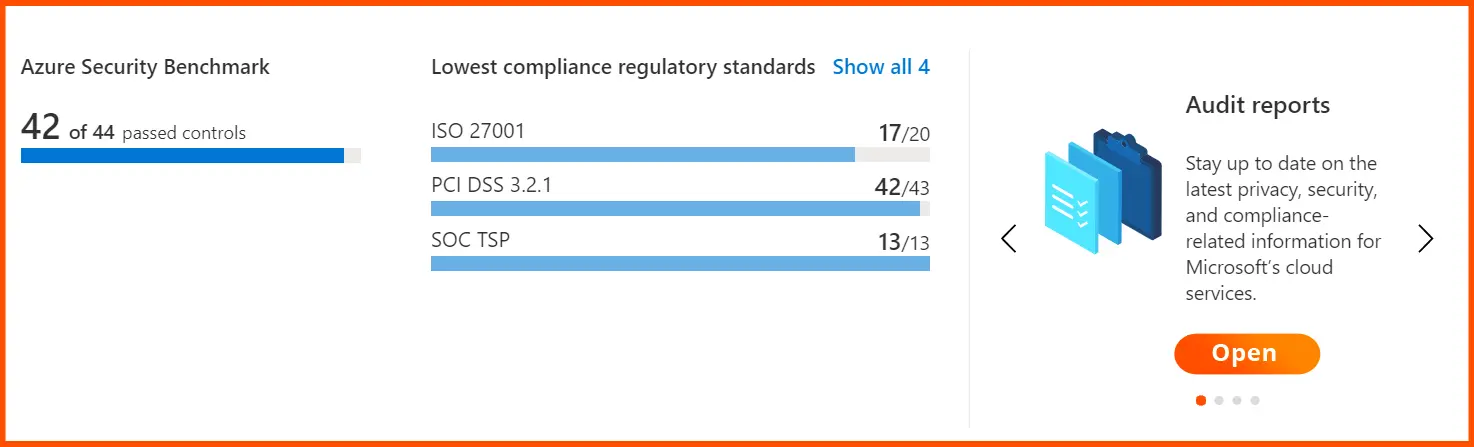
For instance, the Azure Security Benchmark v3 shows the fields below.
Defender for Cloud finds vulnerabilities and gives network suggestions to change configurations and improve security based on best practises for network security. The network live map allows you to view all of your networking and recommendations as well as traffic and undesirable connections.
Step 7: Evaluation of Azure Secure Score
In order to make it easier to evaluate the security posture of a deployment, the Microsoft Defender dashboard additionally provides a secure score as a crucial measure. Secure Score can be seen under the Defender menu.
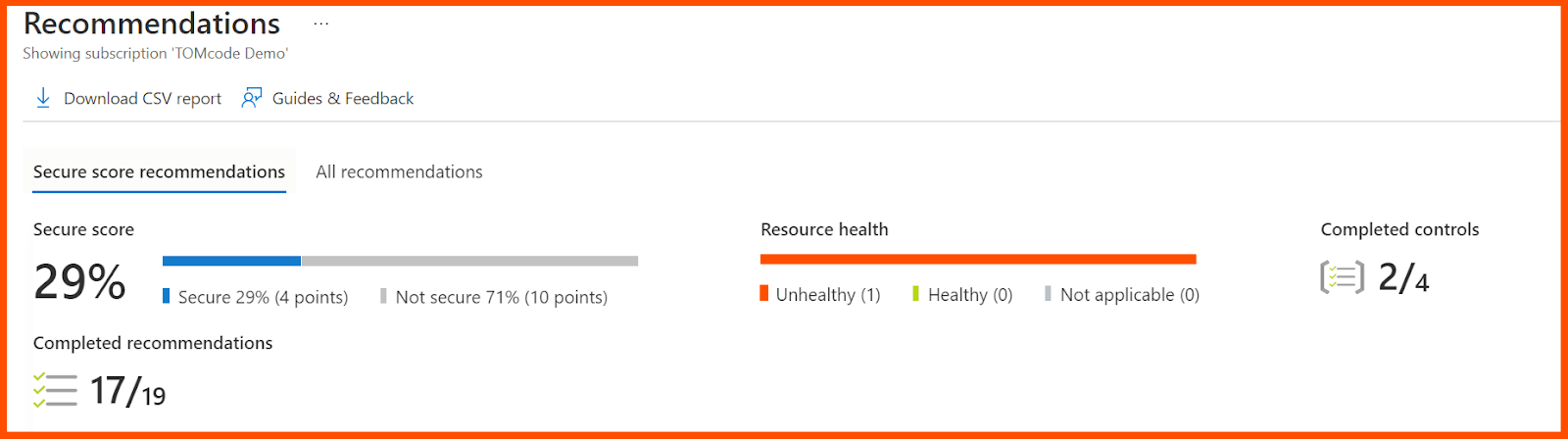
Now, click on the Recommendations to view the scores for all resources, as shown below.
Step 8: Adding Azure Security Centre to a CI/CD Pipeline
Administrators may check the status of workloads and access sophisticated options for effective pipeline management using Microsoft’s Defender for Cloud, which comes pre-loaded with a variety of partner security solutions.
Support for multiple third-party security data and event management (SIEM) solutions is one of these features offered by Azure Defender. DoC provides teams with an export option that allows them to send warnings to well-known SIEM systems like IBM QRadar XDR and Splunk in order to connect with them.
First, as shown below, select the Security solutions option from the Microsoft Defender for Cloud menu.
Step 9: Setting up the Event Hub
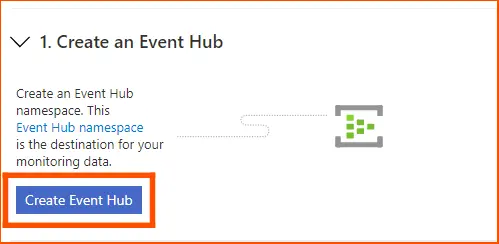
The Event Hub, a namespace that compiles all of Azure’s monitoring data, could possibly be ingested by SIEM systems, providing seamless interaction with the monitoring platform.
Press the Create an Event Hub button on the SIEM integration page.
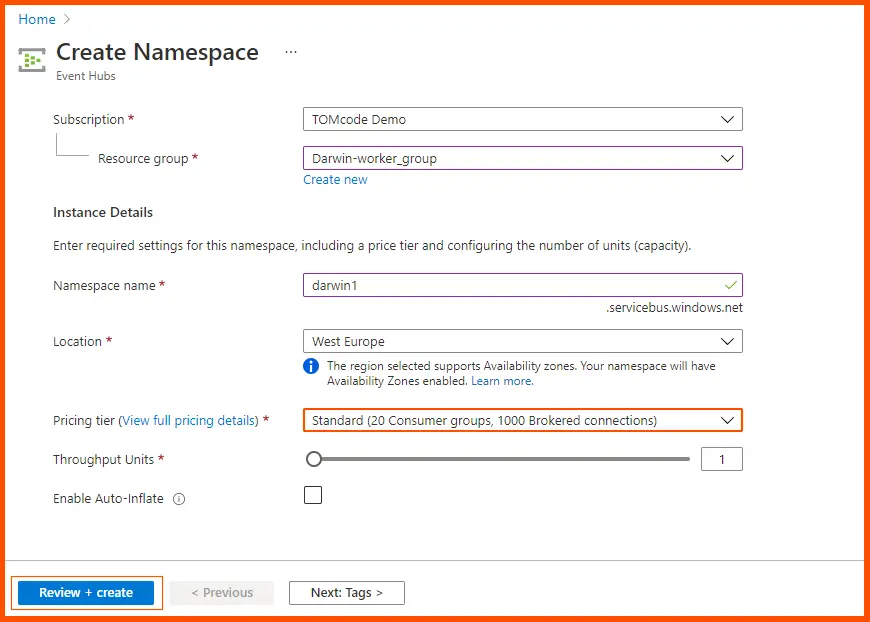
This leads to a page for creating namespaces. After naming the namespace, click Review + Create.
The dashboard shows Requests, Messages, and Efficiency for Azure resources when the name space has been defined. The namespace is an access policy-related logical grouping of event hubs.
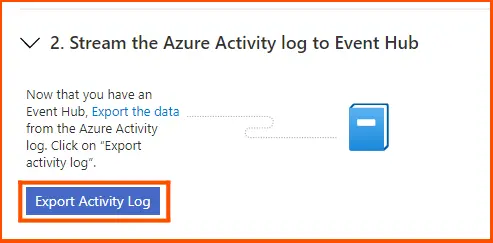
Click Export Activity Log to download Azure logs to the event hub from the SIEM integrations page. A list of workspaces and subscriptions that qualify for onboarding may be seen on the Upgrade tab.
Choose Upgrade to turn on all Microsoft Defender for Cloud security capabilities after selecting the subscriptions and workspaces you want to upgrade from the list of subscriptions and workspaces you want to secure with Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
A large number of tools and capabilities that are more advanced than those in the basic free edition of Cloud Defender are included in the upgraded premium version. The improved version was created by Microsoft as a complete security management and threat protection solution that works with hybrid cloud workloads.
FAQs
What is the difference between Microsoft 365 Defender and Defender for Cloud?
Office 365 Cloud App Security only supports the Office 365 app connector, but it has access to all of Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps’ features. The same interface used for Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps also allows access to Office 365 Cloud App Security. It is included in the Office 365 E5 plan.
Does Microsoft Defender for Cloud have antivirus software?
Yes, multicloud security programme is called Microsoft Defender for Cloud. It supports threat protection across various platforms and offers native cloud security posture management (CSPM) features for Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud environments.
How to protect the security of the cloud?
The cloud security can be improved by means of the following ways:
- Usage of an encrypted cloud service.
- Check out the User Agreements.
- Configure Your Privacy Settings.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication and strong passwords.
- Not sharing sensitive information and personal information with others
- Implementation of a Powerful Anti-Malware Programme
Summary
Cloud security is an ongoing process, and it needs constant monitoring and adaptation to emerging threats. Maintaining a secure cloud environment requires putting cloud security best practices into practice, such as activating multi-factor authentication, imposing strict access rules, and routinely updating your security setups.
You may improve your organization’s security posture and safeguard your crucial assets from potential cyber threats by utilizing Microsoft Defender’s capabilities and its cloud security features. To hone your practical skills, Whizlabs offers hands-on labs and sandboxes and you can play around with the chosen cloud platform.
If you have any queries on this blog post, please feel free to comment us!
- Top 20 Questions To Prepare For Certified Kubernetes Administrator Exam - August 16, 2024
- 10 AWS Services to Master for the AWS Developer Associate Exam - August 14, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Machine Learning Specialty Certification - August 7, 2024
- Best 15+ AWS Developer Associate hands-on labs in 2024 - July 24, 2024
- Containers vs Virtual Machines: Differences You Should Know - June 24, 2024
- Databricks Launched World’s Most Capable Large Language Model (LLM) - April 26, 2024
- What are the storage options available in Microsoft Azure? - March 14, 2024
- User’s Guide to Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine - March 1, 2024