Data storage has been considered a real problem within IT enterprises in the present era. But, with the introduction of AWS cloud, data storage problems seem to soon get eradicated completely. Thus, it is quite important for people to gain insight into the Amazon Elastic Block Storage and Balancer and it’s attributes before they can take concern upon implementing it.
In this article, you will know about some of the core details and fundamentals associated with Amazon EBS and Amazon Elastic Load Balancing.
Go through complete guide of Virtual Private Cloud today!
What is Amazon Elastic Block Store?
Amazon Elastic Block Store is a block-level space for data storage that is meant to work collaboratively with EC2 instances. When the EC2 instances are jammed up with EBS, the volumes are used for storing specific file systems. Not just that, but EBS is also used for hosting OS and applications for specific organizational purposes.
For ensuring high availability, every provisioned EBS volume is automatically visible within other storage spaces that have the same Availability Zone within AWS Region. With this measure, AWS ensures 99.9% availability of data for the users. Along with that, Amazon Elastic Block Storage is also offering data encryption with the use of customer or Amazon-managed keys through the KMS service aspects of AWS.
What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancing?
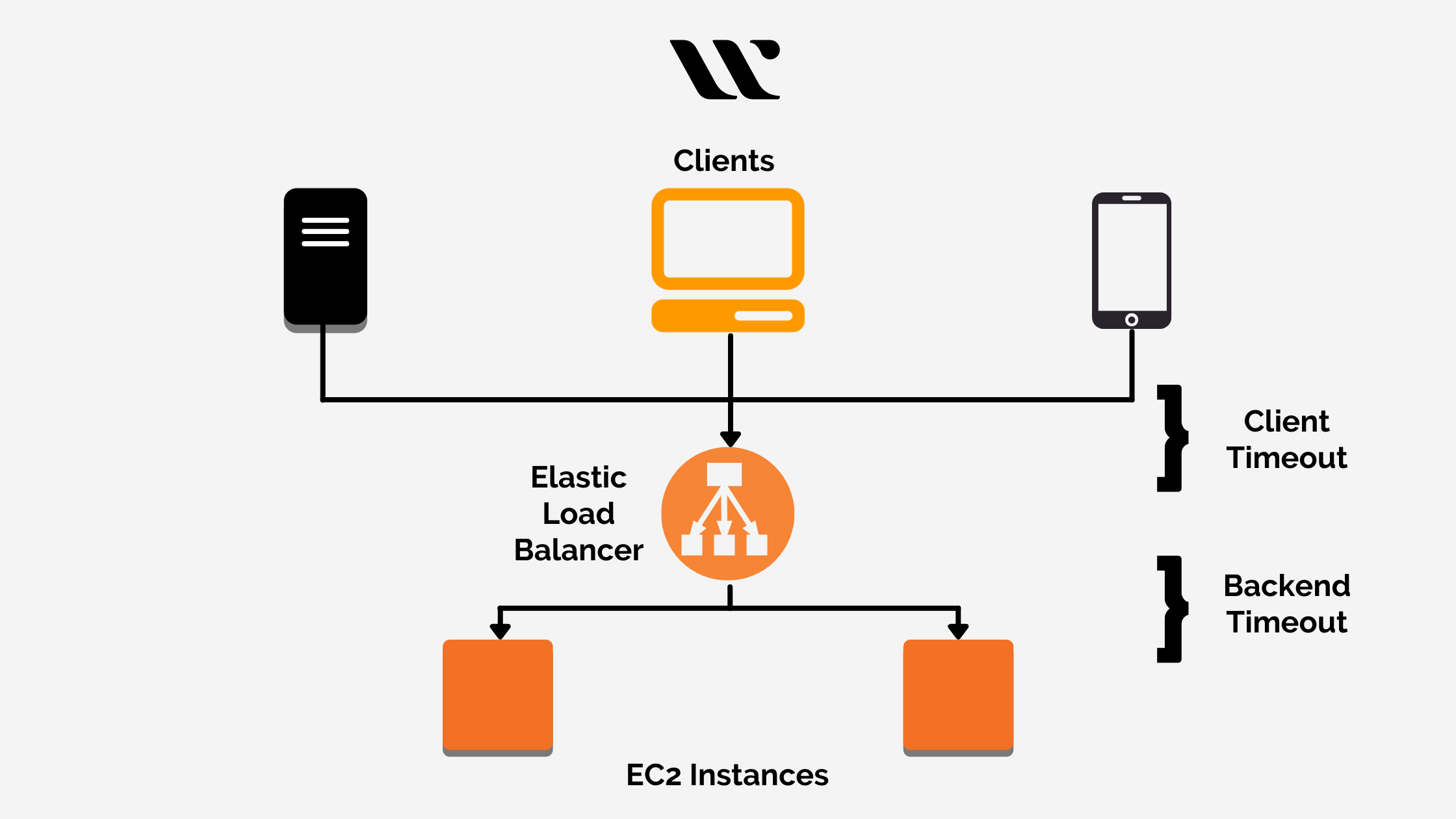
The use of Elastic Load Balancers is meant to automatically distribute the application traffic across diverse targets such as IP addresses, virtual appliances, EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and containers. It has the potential to handle the fluctuating load upon the app traffic within the single or multiple availability zones.
Amazon Elastic Load Balancing service offers four load balancers to carry out the features of auto-scaling, high-availability, and high-end security for ensuring eradication of faults within your application. The four load balancers are Classic Load Balancers, Gateway Load Balancers, Network Load Balancers, and Application Load Balancers.
The best part is that Amazon allows you to migrate from one load balancer to another seamlessly if your application seeks more efficiency. For instance, if you are currently on the application load balancer, then you can migrate to the network or application load balancer by selecting the ideal options within the AWS console.
Read more on AWS Virtual Private Cloud now!
Types of AWS Elastic Block Store Volumes
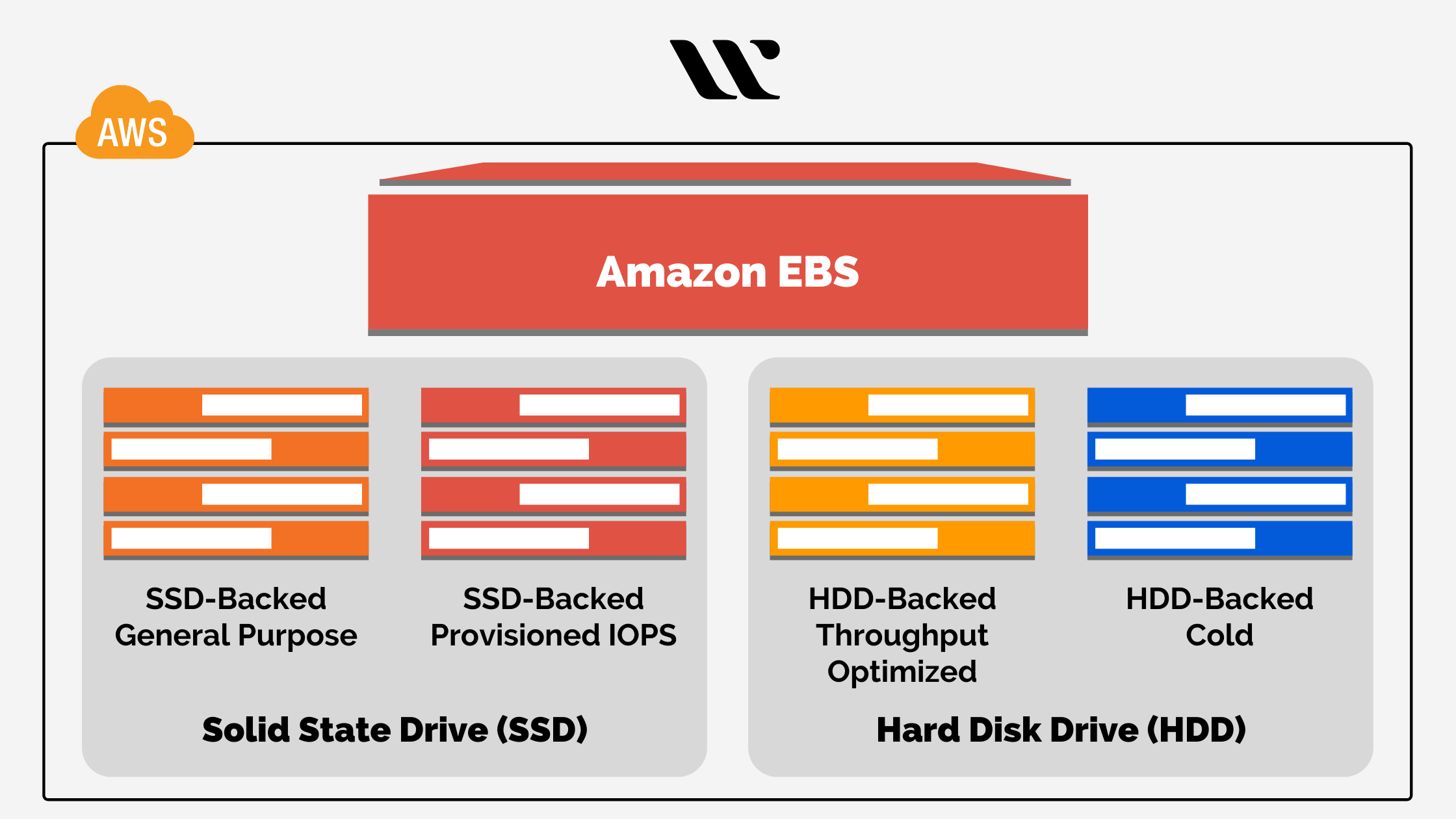
Before you can understand the combined potential of Amazon Elastic Block Storage and Balancer, it is important that you understand their aspects separately. Starting with EBS, it has two types of volumes that are mainly used for the select applications that are SSD and HDD.
SSD (Solid State Drives) consists of two sub-sets that include General Purpose SSD and Provisioned IOPS SSD. The General Purpose SSD is meant to offer balance in terms of performance and economy upon the applications or instances. In contrast, the Provisioned IOPS SSD is meant for enhancing the performance of specific essential applications.
HDD (Hard Disk Drives) consists of two sub-sets that include Throughput optimized HDD and Cold HDD. Throughput Optimized HDD is quite inexpensive and is meant for high and rigorous use. It has the potential to handle intensive workloads imposed upon it. Cold HDD is considered an even cheaper option for instances with considerably fewer accessibility needs.
Types of Elastic Load Balancers
As stated above, there are four elastic load balancers embedded within the functionality to offer adequate balancing in terms of directing the application traffic to healthy instances. These load balancers have different significance in order to help the users choose one as per their requirements and ease of use.
Application Load Balancer is a Layer 7 Type Balancer that targets EC2 instance, IP, and Lambda. It allows termination of the proxy behavior and supports protocol listeners such as gRPC, HTTPS, and HTTP.
Network Load Balancers is a Layer 4 Type Balancer that targets EC2 Instances and IP. It also allows termination of the flow or proxy behavior and supports protocol listeners such as TLS, UDP, and TCP.
Gateway Load Balancer is of combination type blended with Layer 3 Gateway and Layer 4 Load Balancing. Moreover, it targets both IP and Instances without the ability to terminate the proxy behavior or flow. It also supports only IP as a prime protocol listener.
Classic Load Balancer is of Layer 4 or 7 Type Balancer with no target type but has the potential to terminate the flow within the functionality. The best aspect of this load balancer is that it supports all types of protocol listeners such as TCP, SSL, TLS, HTTPS, and HTTP.
Features of Amazon EBS and Load Balancing Attributes
With the basic knowledge gained about the potential of both of these important AWS services, it is important for you to understand the features of Amazon Elastic Block Storage and Balancers to judge the combined potential for your business expertise.
The features of Amazon EBS are:
- High Availability of EBS Volume- You can create an EBS volume within a select Availability Zone, after which you can attach to a respective instance within that Zone. If you wish to enhance that volume’s availability, you can create a specific snapshot to store it again on another volume within that region. With it, you can easily leverage the potential of the high availability of Amazon EBS volumes within diverse AWS regions. Moreover, it will help you avail yourself of features and facilities such as geographical expansion, disaster recovery, data center migration, and others.
- Encryption to EBS Volumes- With Amazon Elastic Block Storage, you can seek encryption upon the volumes to meet your requirement of enhanced security to certain applications or data that needs regulated access. Therefore, when you create an EBS volume with encryption, you will have to attach it to the supporting type of instance, after which all the data that is stored at rest, snapshots, and disk I/O will get encrypted within that volume. This encryption is initiated within the hosting servers of EC2 instances. It helps with the encryption of data while it is being moved from EC2 instances to the Amazon EBS storage.
- Point-In-Time Snapshots- With Amazon EBS, you are destined to come up with the creation of point-in-time snapshots for the respective volumes. These snapshots are persisted to S3 and are usually meant for the long-term durability of the data. Moreover, these snapshots can also be used as a starting point for the following new volumes of EBS. You can make use of the same snapshot for creating and launching several new EBS volumes without any restrictions.
- Monitoring Aspects- With the help of Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Management Console, you can check or monitor the volume performance for the aspects such as throughput, latency, average queue length, bandwidth, and others. It will help you be aware of implementing enough performance to the respective applications.
The features of Amazon Elastic Load Balancing are:
- Security- While creating the Virtual Private Cloud over AWS, you can pick the Security Groups that are supposed to offer security and networking assistance for Elastic Load Balancing aspects. These security aspects are primarily meant for Classic and Application load balancers. Moreover, you can also seek configuration of such balancers to either be internet-facing or non-internet-facing with private IP.
- Enhanced Throughput- The Elastic Load Balancers are meant to handle traffic on a growing scale. They have the potential to implement load balance for over millions of requests every second. Moreover, specific balancers can also handle sudden peaking traffic patterns as well.
- Rerouting of Traffic upon Healthy Targets- Elastic Load Balancers have the built-in feature to track down the health of specific targets before directing the traffic onto them. In case the instance is not healthy or damaged, the balancer will reroute the traffic to a healthy instance until it is fixed.
- Operational Logging & Monitoring- With the use of Amazon CloudWatch, the metrics upon the load balancers will be available within the AWS Management Console. These metrics will be mostly upon the error counts, type of errors, latency upon requests, and other such aspects.
Conclusion
With these clear explanations of the definition and features of Amazon Elastic Block Storage and Balancer, you might have gained some knowledge about their implementation and productivity. If yes, you can definitely go ahead and integrate them to ensure that your application gets enough performance. Also, the traffic gets directed adequately to them by combining the use of Elastic Block Storage and Balancer.
Have you checked out 40+ Best Performing Free Tests from Whizlabs!
There are more features embedded within the functionalities of these two services by AWS. You need to dive into it to know more about how it can enhance your productivity.
- Top 20 Questions To Prepare For Certified Kubernetes Administrator Exam - August 16, 2024
- 10 AWS Services to Master for the AWS Developer Associate Exam - August 14, 2024
- Exam Tips for AWS Machine Learning Specialty Certification - August 7, 2024
- Best 15+ AWS Developer Associate hands-on labs in 2024 - July 24, 2024
- Containers vs Virtual Machines: Differences You Should Know - June 24, 2024
- Databricks Launched World’s Most Capable Large Language Model (LLM) - April 26, 2024
- What are the storage options available in Microsoft Azure? - March 14, 2024
- User’s Guide to Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine - March 1, 2024